Last topic of the chapter chemical kinetics is the theory of collisions which is a frequently asked concept in JEE MAINS. This concept was discovered in the early 20th century by Max Trautz and William Lewis in the year 1916 and 1918 respectively. The scientists came up with a proposal that if the molecules are aligned in a positive symmetry and overcome the energy barrier threshold, an effective collision will take place which affects the rate of the chemical reaction.
For more details related to the concepts of collision theory, you can proceed with the article given below.
Relevant Suggestion: NCERT Solutions
- What is Collision Theory?
- Activation Energy
- Orientation Factor
- Temperature Dependence
- Arrhenius Equation
- Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution
- Effect of Catalysts
- Class 12 Chemistry Notes for Important Chapters
- Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
What is Collision Theory?
Collision theory is a concept which states that the rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the collision of the molecules. Higher the kinetic energy of the molecules reacting with each other, higher will be the impact of the collision, leading to a higher speed of the reaction.
It can be mathematically represented through the equation:
Where:
p: steric factor (orientation probability, 0 < p ≤ 1)
Z: collision frequency
e−Ea/RTe^: fraction of collisions with sufficient energy
For understanding this topic briefly, let us dive into some related key terms which will help clear our basic concepts.
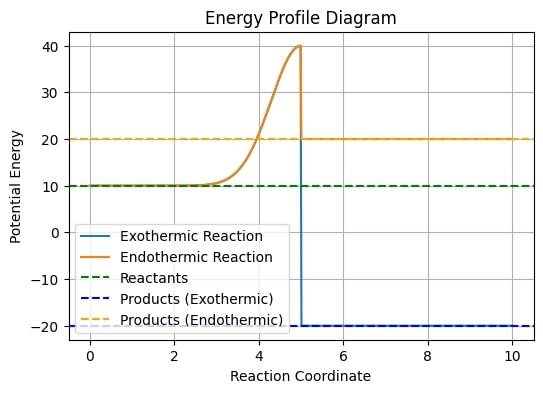
Activation Energy
For a particular reaction to take place, the particles must possess a certain amount of kinetic energy, below which the desired reaction won’t be possible. This minimum amount of energy required for the occurrence of a reaction is called activation energy. A higher amount of activation energy (Ea) will lead to a stronger collision between the particles which will eventually speed up the reaction. Hence, only those collisions will end up in a reaction whose kinetic frequency is equal to or greater than the Ea.
In simple terms;
If Kinetic Energy < Ea, molecules will bounce back and no reaction occurs
If Kinetic Energy > Ea, reaction will take place and a new product will be formed
Orientation Factor
Even if activation energy is high, not all collisions between the molecules of an equation will result in the generation of energy. Another factor that comes into account in this case is known as the orientation energy, which states that the particles must be aligned in a proper symmetry or direction so that effective collisions happen and chemical reactions can take place.
Orientation factor is also known as steric factor (p) and is represented by the mathematical equation:
k=p⋅Z⋅eRT−Ea
Where:
k = rate constant
p = orientation/steric factor (0 < p ≤ 1)
Z = collision frequency
Ea = Activation energy
R = gas constant
T = temperature
E = Euler’s number
This equation is known as the modified Arrhenius Equation.
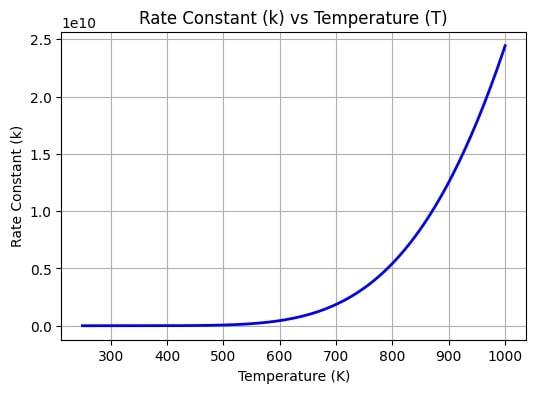
Temperature Dependence
Rate of a chemical reaction is highly influenced by the temperature. The concept of temperature dependence states that a high temperature will increase the kinetic energy of the molecules. These molecules will then collide with each other more frequently and at a faster rate which can lead to more number of strong reactions. In simple terms,
High Temperature = Higher Rate of reaction
To summarize the above concepts; Arrhenius equation, collision theory and temperature dependence are concepts interlinked to each other.
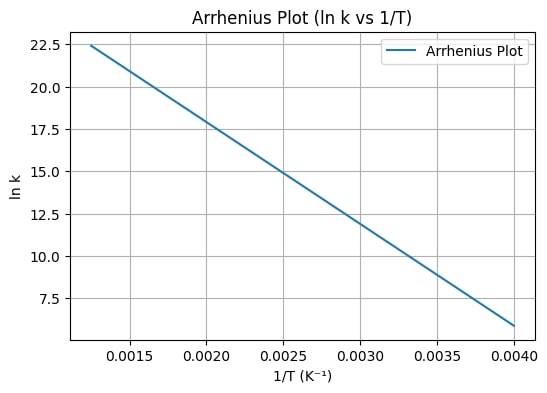
Arrhenius Equation
This formula states that the change in the temperature is directly proportional to the rate of the chemical reaction. A higher temperature means more kinetic energy of the particles leading to a higher collision rate, eventually speeding up the reaction process.
Mathematical representation:
where:
: Rate constant.
: Pre-exponential factor
: Activation energy
: Gas constant ( ).
: Absolute temperature (K).
: Euler’s number
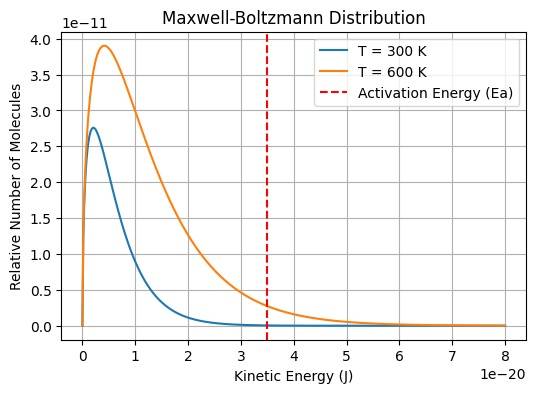
Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution
The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution is one of the most important concepts of chemical kinetics and is used to solve a wide range of numerical problems. This equation is used to calculate the exact energy of a particular molecule at a specific interval of time. Different molecules in a gas have different speeds at different points of time, and Maxwell-Boltzmann equation is used to calculate the energy of the desired molecule at a given temperature.
The probability that a particular molecule has an energy E at a specific point will be:
f(E)=π2((kT)3/21)E1/2e−kTE
Where:
f(E): probability density function for kinetic energy
E: kinetic energy
k: Boltzmann constant (1.38 × 10⁻²³ J/K)
T: absolute temperature (K)
Effect of Catalysts
Catalysts are substances which are used to affect the speed of a chemical reaction by altering the existing pathway and lowering the activation energy without themselves being consumed in the process. Due to the lower activation energy, more number of collisions will be able to occur as the particles will have more kinetic energy, eventually leading to a higher collision rate.
They don’t have any side effects on the reactants or the products and are only used to affect the rate of the reaction.
Through the Arrhenius equation,
k=AeRT−Ea
Low Ea will increase the rate constant k, causing more number of effective collisions to take place.
Click to Read: NCERT Chapter 3 Chemistry: Chemical Kinetics
Class 12 Chemistry Notes for Important Chapters
Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
Commonly asked questions
What is the significance of molecular orientation in collision theory?
For a collision to happen, the molecules must collide with each other at a high frequency. But the result can still lead to disappointment. This is because even if molecules collide effectively, they also need to be aligned properly in symmetry. Only this can help in the formation of new bonds. Hence, the molecular orientation is considered important in he concept of collision theory.
What happens if a collision fails?
Successful collisions help in the formation of new products, whereas in unsuccessful collisions the molecules just bounce back without causing any reaction. In such cases, the reaction fails and no new product or bond is formed.
What will happen if the substance to be reacted is unimolecular?
Unimolecular Reactions might seem to not participate in the collision theory due to the presence of only a single molecule. In such cases, the molecule is activated by external forces such as heat, light, electricity, or by colliding with the walls of the container. This force charges the molecule enough to break the activation barrier and result in an effective collision.
Chemistry Chemical Kinetics Exam