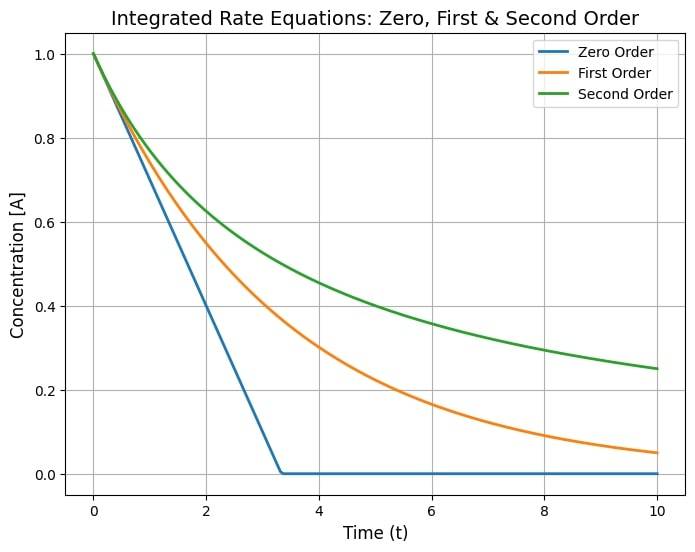
Next topic which we are going to cover under the chapter Chemical Kinetics is integrated rate equations. The main aim of these equations is to calculate the exact amount of reactant at a particular time frame of the reaction process. These equations help us calculate the concentration of a reactant at any specific interval of time along with determining the half life and order of the reaction, which that will be covered in this article.
Candidates who wish to score well in JEE MAINS must go through this topic thoroughly and understand the core fundamentals of integrated rate equations for solving numerical problems. Let’s dive into each of these concepts individually.
Relevant Suggestion: NCERT Solutions
- What are Integrated Rate Equations?
- Zero-Order Reactions
- Derivation for Zero-Order Reactions
- What is Half Life for Zero Order Reaction?
- First-Order Reactions
- Derivation for First-Order Reactions
- What is Half Life for First Order Reaction?
- Second-Order Reactions
- Derivation (Square of a Single Reactant)
- Derivation (Product of 2 Reactants)
- What is Half Life for Second Order Reaction?
- Difference between Order of a Reaction and Molecularity of a Reaction
- Class 12 Chemistry Notes for Important Chapters
- Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
What are Integrated Rate Equations?
Integrated Rate Equations are mathematical equations which are used to determine how the concentration of reactants change in a chemical reaction over a certain duration of time. These equations can vary depending upon the order of reactions and the rate of a reaction. The general representation of an integrated rate equation as per the rate law can be given by:
-d[A]/dt = k[A]^n
Where n = order of the reaction (zero, first or second)
Now, let us study these orders of a reaction one by one.
Zero-Order Reactions
In such a type of reaction, the value of k(reaction aret) remains constant irrespective of the reactant's concentration. Mathematical representation of zero order reactions can be given by:
−d[A]/dt=k
Where, A = Concentration of the reactant A
And k = rate constant for zero order reaction
After integration of the above equation, we get
[A] = [A]` - kt
Where,
[A]` = Initial concentration of the reactant
[A] = concentration of the reactant at time t
k = rate constant
Derivation for Zero-Order Reactions
For a reaction , the rate law states that:
d[A]=−kdt
Now integrate both sides of the equation,
Hence, we get the final equation as [R]=[R]0−kt
where is the initial concentration at .
And [R] is the concentration at time t.
What is Half Life for Zero Order Reaction?
The Half-Life of a reaction is referred to as the amount of time in which the concentration becomes half of what its original value was.
Mathematical formula for Half Life is given by:
t₁/₂ = [R]₀ / 2k
First-Order Reactions
These are the type of reactions where the rate of reaction is proportional to the concentration of only 1 single reactant. Mathematical representation for a First order reaction can be given by:
−d[A]/ dt=k[A]
Where, [A] = Concentration of the reactant A at time t
And k = rate constant for first order reaction
Integrating the above equation, we get
[A] = [A]'e^-kt
Derivation for First-Order Reactions
For a reaction , the rate law is depicted by:
Further integrating both sides of the equation, we get:
∫[A]0[A][A]d[A]=−k∫0tdt
ln[A]−ln[A]0=−kt
Combining the log values, we get:
ln([A]0[A])=−kt
[A]=[A]0e−kt
Hence, proved
What is Half Life for First Order Reaction?
Half Life of a first order reaction is depicted by:
ln([A]0/2[A]0)=kt1/2
ln2=kt1/2
t1/2=0.693/k
Second-Order Reactions
Derivation (Square of a Single Reactant)
Derivation (Product of 2 Reactants)
What is Half Life for Second Order Reaction?
Difference between Order of a Reaction and Molecularity of a Reaction
Class 12 Chemistry Notes for Important Chapters
Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
Commonly asked questions
What is the importance of integrated rate equations?
These are the important highlights of integrated rate equations:
- predict the rate of a reaction
- calculate order of reaction (zero, first, second)
- understand mechanism of a reaction
- compute half life
- calculate the value of k
What is a Pseudo Order reaction?
This is the type of reaction which bheavies like a first order reaction inspite of being a higher order reaction (second or third). This happens due to a particular reactant being present in an excessive quantity thorughout the chemical reaction.
Why is half-life of a first-order reaction independent of concentration of the reactant?
To understand the phenomenon behind this, have a close look at the formula of the first order reaction.
t1/2 = 0.693/k
Here, we can see that the half life is only dependent on k (rate constant) since there is no [A]' in the formula. Hence, we can easily conclude that the half life of a first order reaction is independent of the initial concentration [A]'.
Chemistry Chemical Kinetics Exam