Ever wondered why people use passed away instead of died or let go instead of fired? Well, that’s because they want the listeners or readers to accept such unpleasant news pleasantly. Here, Euphemisms come to their rescue. Euphemism refers to the use of words or phrases to describe an embarrassing scenario mildly or less offensively. In simple words, Euphemism is the replacement of harsh or rude words with lighter and polite words. It is commonly used to address sensitive or offensive topics such as death, religion, sex, social or economic hardships.
For example, when Jack in the movie Titanic said, “See, my folks died in a fire when I was fifteen, and I’ve been on the road since.”, he used on the road Euphemism to express that he has been travelling for a long time. Another example for Gen Z, the most commonly used word nowadays, "Pookie", serves as an Euphemism for direct endearments such as cute, honey, or sweetheart.
Though Euphemism may not be a part of the syllabus for English grammar in schools, it is a part of the syllabus in several entrance and competitive exams. Let’s know what is Euphemism with examples, its definition, a list of words and practice exercises with answers.
- What is Euphemism Figure of Speech?
- Definition of Euphemism in English
- Commonly Used Euphemisms: List of Words
- Usage of Euphemisms in English Language: When to Use & When Not to
- Examples of Euphemism in a Sentence
- Importance of Euphemisms in Education
- Euphemism & Other Figures of Speech
- Best Books on Euphemisms in English
- Euphemism Worksheet with Answers
- FAQs Regarding Other Figures of Speech
What is Euphemism Figure of Speech?
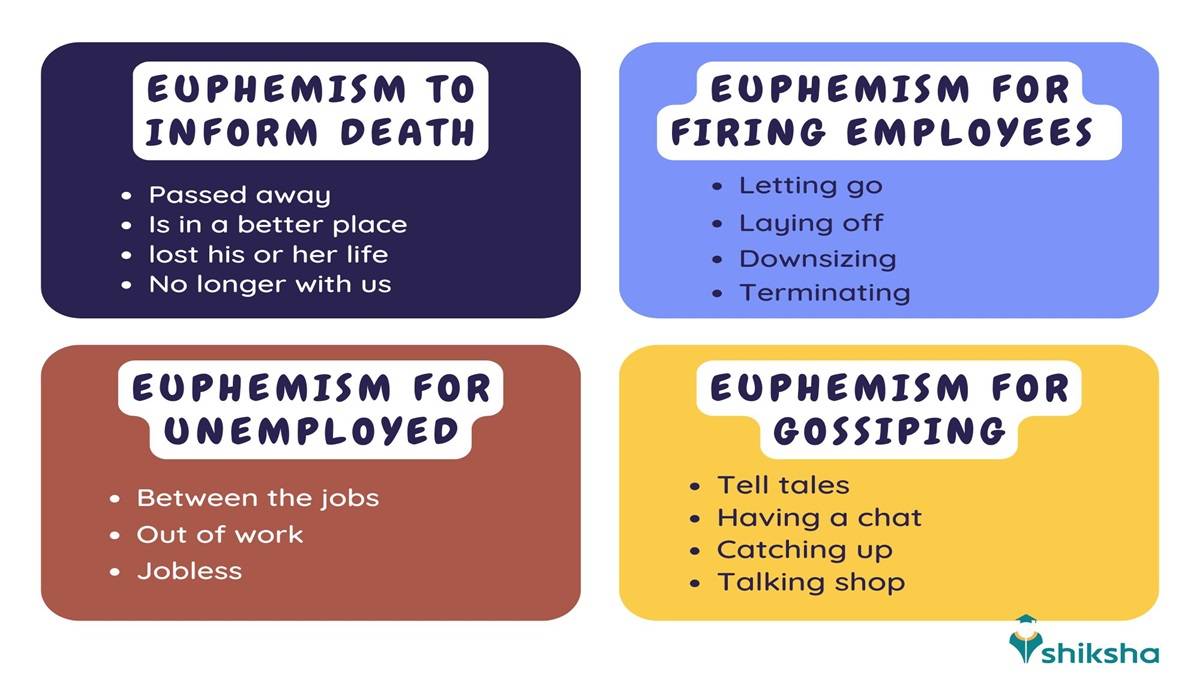
Euphemism is one of the figures of speech in English Grammar. Euphemisms are the words or phrases that are used to describe offensive or unpleasant situations in a mild and more suitable manner. These words enable communication of unpleasant news or negative feedback in an acceptable way. For instance, in corporate layoffs, employers choose to say ‘You are being let go’ instead of ‘You are being fired’ to the employees. The image shared below will help you understand the topic better.
Also Read: Adverbs of Degree
Definition of Euphemism in English
According to Collins Dictionary, Euphemism is defined as “an inoffensive word or phrase substituted for one considered offensive or hurtful, esp one concerned with religion, sex, death, or excreta. Examples of euphemisms are sleep with for have sexual intercourse with; departed for dead; relieve oneself for urinate”
According to Oxford Learner’s Dictionaries, “euphemism (for something) is an indirect word or phrase that people often use to refer to something embarrassing or unpleasant, sometimes to make it seem more acceptable than it really is”
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, Euphemism is “a word or phrase used to avoid saying an unpleasant or offensive word”
Pronunciation: ˈjuːfɪˌmɪzəm
Also Read: Definition of Punctuation Marks
Commonly Used Euphemisms: List of Words
There are several Euphemisms used in day-to-day life that enable decent communication by softening the blow of unpleasant topics. Have a look at the list of euphemism words along with their meaning below:
| Words or Topics |
Euphemism Words |
|---|---|
| Death |
Passed away, departed, resting in peace, left for heavenly abode, gone to a better place |
| Firing employees |
Let go, layoff, downsizing, release of duties |
| Toilet |
Washroom, restroom, powder my use, comfort station |
| Poor |
Financially challenged, economically disadvantaged |
| Ugly |
Unique looking, not traditionally attractive, distinctive |
| Fat |
Curvy, Big boned, full-figured, well-fed |
| Short |
Vertically impaired or challenged |
| Old |
Senior citizen, mature, seasoned, golden years, over the hill |
| Used goods |
Pre-owned, previously enjoyed |
| Lying |
Telling stories, Economical with the truth, stretching the truth, alternative facts, fabrication |
| Sex |
Make love, intimate, sleeping together, hooking up, getting lucky, knocking boots |
| Primary income earner |
Breadwinner, Bringing home the bacon |
| Financially secure |
Living comfortably, well-to-do |
| Civilians killed in war |
Collateral damage |
| Homeless |
On the streets, down-and-out |
| Rich |
Well-to-do, well-off |
| In debts |
Negative cash flow |
| Anger/ Angry |
Blow a fuse, To get off the deep end, To blow a gasket |
| Housewife |
Homemaker, domestic engineer |
| Husband or Wife |
Spouse, life partner |
| Pregnant |
Bun in the oven, in a family way |
Also Read: List of Prepositions Words
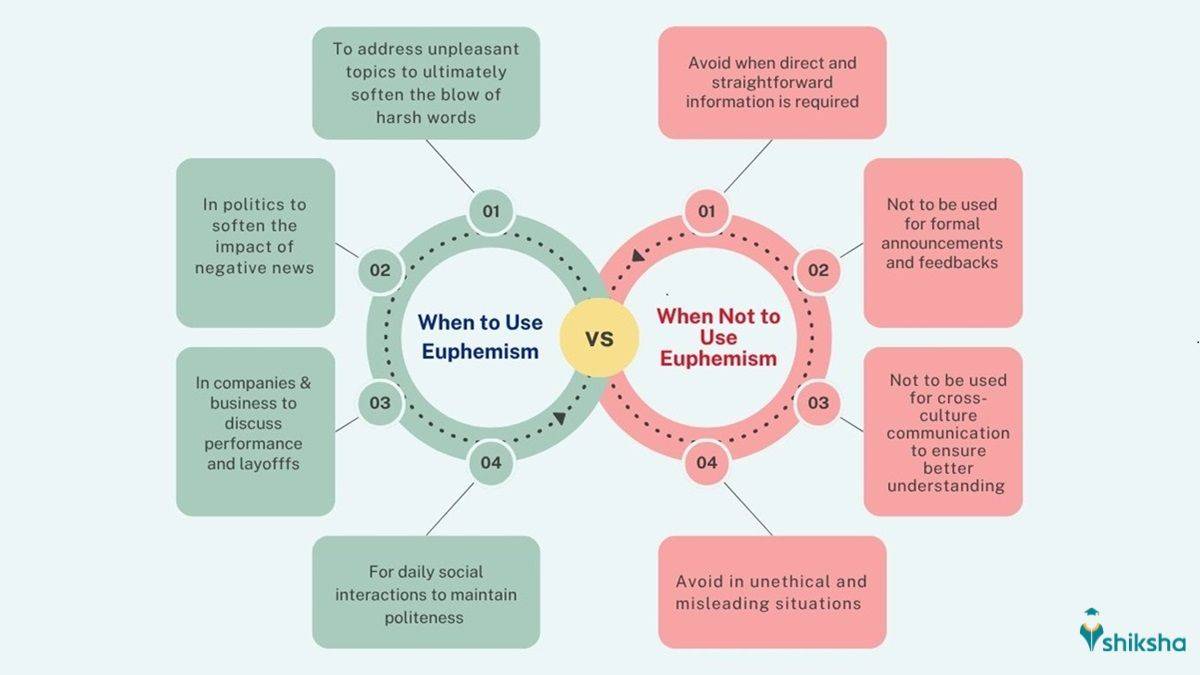
Usage of Euphemisms in English Language: When to Use & When Not to
Besides replacing harsh and sensitive topics with pleasant language, Euphemisms are used in other situations as well, such as in creative writing or Literature for a natural approach. Moreover, Euphemisms are also used while speaking to children to explain to them a grave situation in a milder way. However, there are situations when Euphemisms should not be used, such as while conveying important information in a formal setting. Have a look at the usage of Euphemism in the English language below and know when to use and when to avoid its use.
Also Read:
Examples of Euphemism in a Sentence
Know the usage of Euphemisms in day-to-day life by going through the examples shared below. These Euphemism examples will make you familiar with the practical applicability of these words or phrases:
- Rohan’s grandfather left for the heavenly abode last week. (died)
- Unfortunately, we have to let you go. (fired)
- It’s difficult for her to understand easily; she has cognitive challenges. (mental illness)
- Jane is currently between jobs. (unemployed)
- Shea was under the influence at the party last night. (drunk)
- Neena is in the family way and will soon be going on maternity leave. (pregnant)
- Many soldiers went missing in action during the war. (likely killed)
- The show was not well received by the producer and was put to bed. (bad and cancelled)
- Shan and Ria parted ways only after one year of dating. (broke up)
- She comes from an affluent family. (rich)
Also Read: Past Perfect Continuous Tense Worksheet with Answers
Importance of Euphemisms in Education
In this day and age, it’s become easier to communicate or have a conversation; however, disagreements still arise from how things are conveyed. It is important to choose the words wisely, as they can influence the perception of the listeners. Euphemisms in the Education sector go beyond formal schooling or learning. It enables the understanding of the English language in a more positive and broader way.
The use of Euphemisms helps teachers and professors in schools and colleges to guide the students in a polite way. For example, instead of saying he has failed the exam, teachers might say he needs more support. The Euphemisms in education help in:
- Creating a more positive environment for learning and training.
- Conveying constructive feedback regarding the student’s growth in a mild way
- Maintaining an honourable relationship between students and teachers
- Communicating politely with the parents regarding difficulties faced by students
Also Read: How to Prepare the Past Perfect Tense?
Euphemism & Other Figures of Speech
There are 20 types of Figures of Speech in the English language, such as Metaphor, Oxymoron, Euphemism, Dysphemism, Smile, Pun, Personification, Hyperbole, etc. Let’s look at the comparison between Euphemism and a few other figures of speech below:
Euphemism and Dysphemism
Euphemism & Dysphemism are opposite to each other. If Euphemism (gentler words) is the use of polite words to convey an unpleasant situation, the Dysphemism (meaner words) is the use of insulting and derogatory terms in place of something usual. Below are some of the situations along with their Euphemism and Dysphemism words to help you better understand the difference between them:
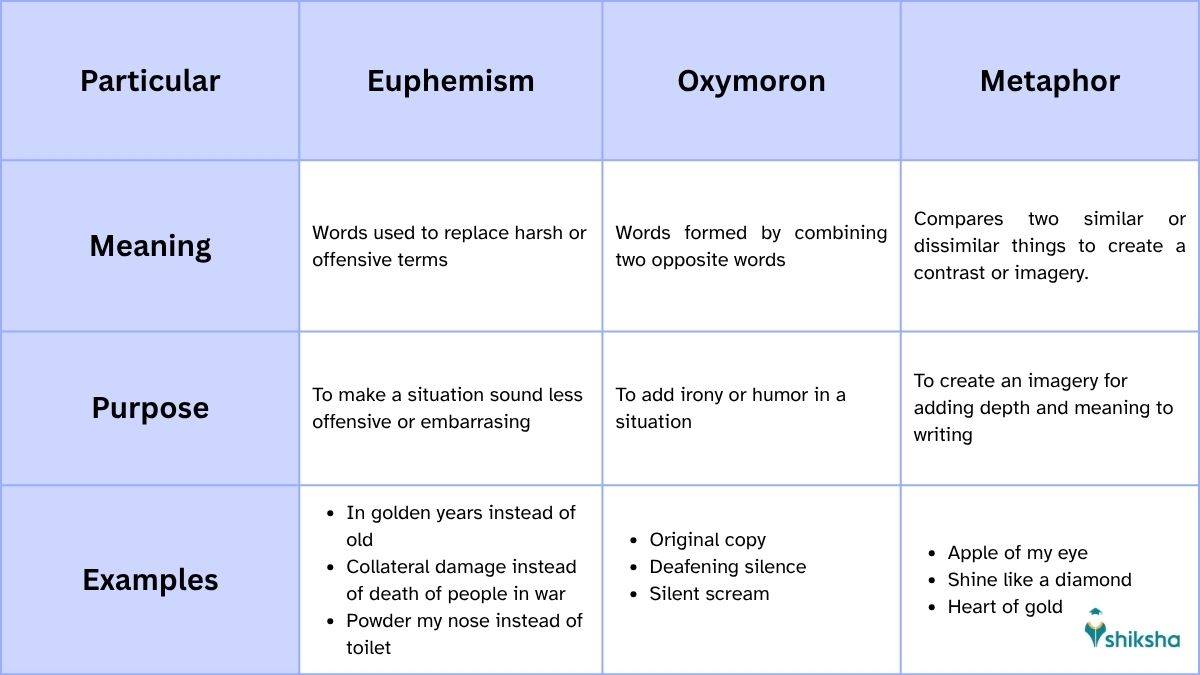
Euphemism, Oxymoron & Metaphor
See the table shared below to understand the difference between Euphemism, Oxymoron and Metaphor:
Also Read: What are Prepositions of Place?
Best Books on Euphemisms in English
Euphemism Worksheet with Answers
FAQs Regarding Other Figures of Speech
Commonly asked questions
Which are some Figures of Speech which are similar to each other?
There are a number of Figures of Speech which are similar to each other but have a subtle difference. Students often get confused between the two, but the confusion and common errors can be mitigated by understanding the differences and regular practice. Some such Figures of Speech are as follows:
· Simile, Metaphor and Personification
· Oxymoron and Paradox
· Paradox and Antithesis
· Hyperbole and Understatement
· Apostrophe and Invocation.
How many types of Figures of Speech are there?
There are broadly over 20 types of Figures of Speech. While around 12 are commonly used in day-to-day communication, rest are used specifically for literature elements such as poems, drama or plays, etc.
What are Figures of Speech?
Figures of Speech are literary devices which add value to a sentence by providing an imagery, special effect and contrasts to create a vivid impact, drama element and improve the reader engagement. Figures of Speech is widely used in literature such as poems, drama or plays, novels, short stories, etc. Apart from that, Figures of Speech are also used in day to day lives and commercial purposes such as advertisement campaigns.
What are the most common Figures of Speech?
Some of the most common Figures of Speech are as follows:
· Simile
· Metaphor
· Personification
· Hyperbole.
This is not the exact or absolute list, but are among the commonly used Figures of Speech.
What is the purpose of using Figures of Speech?
The primary purpose of Figures of Speech is to be more creative and expressive with the language or communication. It also improves the reader experience. Figures of Speech are also to enhance and elevate the language. Moreover, it also adds depth and clarity for the readers. Last but not the least, Figures of Speech adds a touch of humour and comic relief and at times a dramatic effect, which are important components to garner and retain readers' attention.
English Figures of Speech Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds