Carbohydrates are essential biomolecules for the human body. It is obtained from plants and fruits. Examples of carbohydrates are glucose, fructose, sugar cane, etc. Glucose and Fructose are common examples of Monosaccharides. They are also known as simple sugars. The functional group of glucose is aldose and fructose is ketose. Students can refer to the article for detailed differences between glucose and fructose.
To understand the difference between glucose and fructose, students must have a good knowledge of carbohydrates.
Students can refer to the Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 NCERT Solutions to solve the questions based on glucose and fructose. Solving questions based on glucose and fructose will help to understand the key differences between them.
- Define Carbohydrates
- Define Glucose
- Fructose Defination
- Difference between Glucose and Fructose in Tabular column
- Biomolecules in Class 12
- Illustrated Examples from NCERT
- FAQs on Glucose and Fructose
Define Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are biological molecules made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen. The general formula of carbohydrates is Cx(H2O)y. They are also known as saccharides. Based on hydrolysis behaviour, they are divided into Monosaccharides, Oligosaccharides, and Polysaccharides.
Based on the number of carbon atoms and the functional group present, monosaccharides are divided into aldoses and ketoses. Here, Glucose and Fructose fall into the category of Monosaccharides. Carbohydrate foods are fruit, sugar, milk, rice, potatoes, corn, oats, vegetables, whole grains, nuts and seeds.
Read More: NCERT Solutions Class 11 & 12 | NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Solution
Define Glucose
Glucose is a six-carbon sugar that occurs freely and also in combined form in nature. Glucose is present in foods like sweet fruits, honey, starch, and table sugar. Glucose acts as a building block for cellular structures and energy sources for muscles and the brain during physical activity. Glucose is an aldohexose because of has an aldehyde as a functional group.
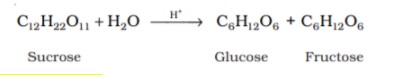
Preparation of Glucose is done in the laboratory either by Sucrose(Cane Sugar) or Starch.
The reaction below is the hydrolysis of the disaccharide, Sucrose, to obtain glucose and fructose in equal amounts.
Fructose Defination
Fructose is a ketohexose due to the ketone as a functional group at carbon number 2. Generally found in fruits, honey and vegetables. Fructose is used as a sweetener for low-calorie foods like carbonated sodas, cereals and yoghurt. Apart from that, it enhances glucose metabolism.
Difference between Glucose and Fructose in Tabular column
Students can check the table for key differences between glucose and fructose.
| GLUCOSE |
FRUCTOSE |
|---|---|
| Glucose is a six-membered ring. |
Fructose is a five-membered ring. |
| Glucose has an aldehyde functional group - Aldohexose. |
Fructose has a ketone functional group - Ketohexose. |
| It forms a pyranose ring structure. |
It forms a furan ring structure. |
| It releases energy fast. |
It releases energy slowly. |
| Glucose is known as Grape Sugar, Dextrose. |
Fructose is known as Fruit Sugar, Levulose. |
| Glucose is produced by the enzymatic hydrolysis of sucrose and starch. |
Fructose is commercially manufactured from sugarcane, corn. |
| Glucose is fatless. |
Fructose has fatty substances. |
| Source: Starch and Table sugar |
Source: Fruits and Vegetables, Sugar Cane |
| It is used for vitamin A production, starch and glycogen. |
It is used to produce ATP and to build glycogen. |
Biomolecules in Class 12
In this chapter on biomolecules, the subtopics are carbohydrates and their types, like mono, oligo and polysaccharides. Further, you can learn about their characteristics and applications in detail. This chapter introduces you to topics like Nucleic acids and proteins.
Illustrated Examples from NCERT
1. Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides. Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, maltose, galactose, fructose and lactose?
Answer: Monosaccharides - Galactose, Fructose, Ribose, 2-deoxyribose
Disaccharides- Maltose, Lactose.
2. Explain why Glucose and Sucrose are soluble in water in comparison to cyclohexane or benzene.
Answer: Both Sucrose and Glucose have OH groups that form intermolecular H-bonds with water. So, because of Hydrogen bonding, they are soluble in water. Cyclohexane or benzene is insoluble because of the absence of Hydrogen bonds.
3. How can you tell the difference between glucose and fructose in a chemical test?
Answer: Seliwanoff's test determines aldose and ketose sugars. When added to the solution, the red colour is formed, and pink in colour when added to the aldoses.
[Image courtesy: NCERT]
FAQs on Glucose and Fructose
Q: What are the functions of carbohydrates?
Q: What is the difference between monomer and monosaccharide?
Q: What is the Glycosidic Linkage?
Q: What are Reducing Sugars?
Q: What are some of the physical properties of Glucose and Fructose?
Chemistry Biomolecules Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Difference between Glucose and Fructose
- Hormones
- Enzymes
- Vitamins
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Difference between Fat and Cholesterol
- Monomeric Proteins
- Difference between Starch and Cellulose
- Structure of Glucose and Fructose
- Functions of Nucleic Acids
- Glycosaminoglycans
- Uses of Ascorbic Acid
- Complex Carbohydrates
- Glycine structure
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test