Screw gauge is an instrument to measure small dimension with precision and high accuracy. It is also known as micrometer screw gauge. The least count of screw gauge is 0.01mm. Similar to micrometer screw gauge, vernier caliper is also used for precise and accurate measurement, although with less precision than a screw gauge. This instrument is used in mechanical engineering, workshops, metalworking, and laboratory applications for precise measurements.
The micrometer screw gauge is an important topic in Class 11 Physics Units and Measurement. Students can focus on screw gauge topic to prepare for the exam. Also, we have provided the NCERT Solution Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 to help students in their board exam preparation.
Also Read:
| NCERT Class 11 notes | |
| CBSE Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Notes |
- What is Screw Gauge?
- Diagram of Screw Gauge
- Formula of Screw Gauge
- Measurement of a Screw Gauge
- Uses of Screw Scale
- Illustrated Examples
- FAQs on Screw Gauge
What is Screw Gauge?
A screw gauge is used to measure the diameter and radius of any metal sheet. It is a U-shaped instrument with a screw attached to it. The fine screw gauge can be difficult to use for rookies.
There are two scales used to measure the units:
- Pitch scale
- Circular scale
The pitch scale is the primary scale and can be seen as a vertical line attached to the instrument. It measures the units in millimetres per revolution. A circular scale is placed horizontally. Half of the millimetre is the circular scale in displacement called a micrometre screw gauge.
Also Check:
| NCERT Solutions | Class 11 Maths NCERT Solution |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics NCERT Solutions | NCERT Solution Class 11 Chemistry |
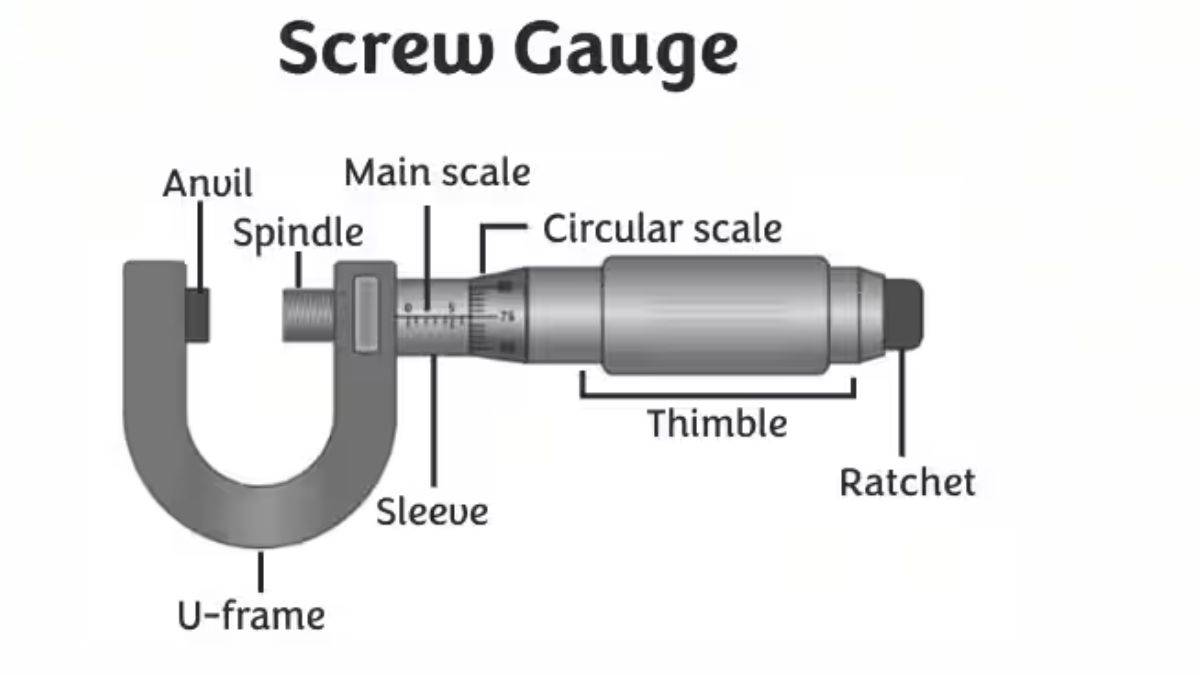
Diagram of Screw Gauge
Below is the illustrative diagram of screw gauge.
Related Materials: Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions | NCERT Solution Class 12 Chemistry | CBSE Class 12 Math NCERT Solution
Parts of Screw Gauge
The important parts of micormeter screw gauge are follwoing:
- Anvil: Fixed part where the object is held.
- Spindle: Movable rod that moves toward or away from the anvil.
- U-frame: Fixed part of screw gauge that holds anvil and spindle.
- Sleeve: Consists of the main and circular scale.
- Thimble: Rotating part that consists of a circular scale.
- Ratchet: Ensure uniform pressure is applied ot the object. It is placed at the end of the thimble.
Formula of Screw Gauge
Screw gauge uses two formulas to calculate the outcome. Either pitch of the screw gauge or least count of screw gauge is used. The third formula is the calculation of the least count of the micrometre and has limited usability.
Pitch of the screw gauge – The pitch of the screw gauge is the ratio between distance moved by a screw and the number of rotations. The formula of the pitch is illustrated below:
- Pitch of the screw gauge = (moving distance by a screw)/ (number of rotations).
Least count of the screw gauge – The least count of the screw gauge can be calculated by the ratio of pitch and the total number of divisions. The formula of least count of screw gauge is as follows:
- Least count of screw gauge = (Pitch)/(number of divisions)
- Least count of micrometer screw gauge = (1 mm)/(100) = 0.01 mm
A micrometre screw gauge can be used to calculate the diameter of a small metal object in millimetres, such as sheets and glass. The formula for the same is shown below:
- Least count of micrometre = (pitch) / total number of divisions
Measurement of a Screw Gauge
So far, we have check the defination of screw gauge, diagram of micrometer, and part of screw gauge. Now we will check how to use screw gauge. Below is the working princle of screw gauge.
How to use screw gauge?
- Some parts of the screw gauge are movable, such as the anvil, sleeve, thimble, ratchet stop, spindle, etc.
- The first step is to clean the spindle and anvil and place the clean cloth between the spindle and anvil. It is preferred to do it to get accurate results.
- After cleaning, the next step is to place the object between the spindle and the anvil.
- To tight the instrument, rotate it in a clockwise direction.
- Lock the thimble and then take the object out after some time.
- Before doing so, write down the reading of the measurement.
Screw Gauge in Class 11
The chapter ‘Units and Measurements’ hold a weightage of seven marks, consisting of two short questions (one mark each) and two short questions (two marks and three marks simultaneously).
Uses of Screw Scale
Using the micrometre screw gauge we can measure
- Thickness of a thin sheet
- Diameter of a small sphere and a thin wire
- Diameter of an irregularly shaped object
Illustrated Examples
1) Explain the formula used to calculate the least count of the screw gauge.
Answer: Least count of screw gauge = (Pitch)/(number of divisions).
2) Write down the formula to calculate the least count of a micrometre.
Answer: Least count of micrometre = (pitch)/total number of divisions.
3) Explain the term ‘Precision Instruments.’
Answer: Precision instruments are the devices that can measure the minimum fraction of mm, e.g., Vernier Callipers and Screw Gauge.
FAQs on Screw Gauge
Q: What is the function of a screw gauge?
Q: What do you understand by the pitch of a screw gauge?
Q: Which two units are used to measure the pitch?
Q: What is the formula to calculate the pitch of the screw gauge?
Q: What are the two essential parts of a screw gauge?
Physics Units and Measurement Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 11th Physics Chapters
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
- NCERT Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Notes
- Physics Motion in Plane
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Physics Motion in Straight Line
- Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Physics Oscillations
- Physics Waves
- Physics Thermal Properties of Matter
- Physics Motion
- Physics Gravitation
- Physics Thermodynamics
- Physics Work, Energy and Power
- Physics Units and Measurement
- Physics Laws of Motion
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test