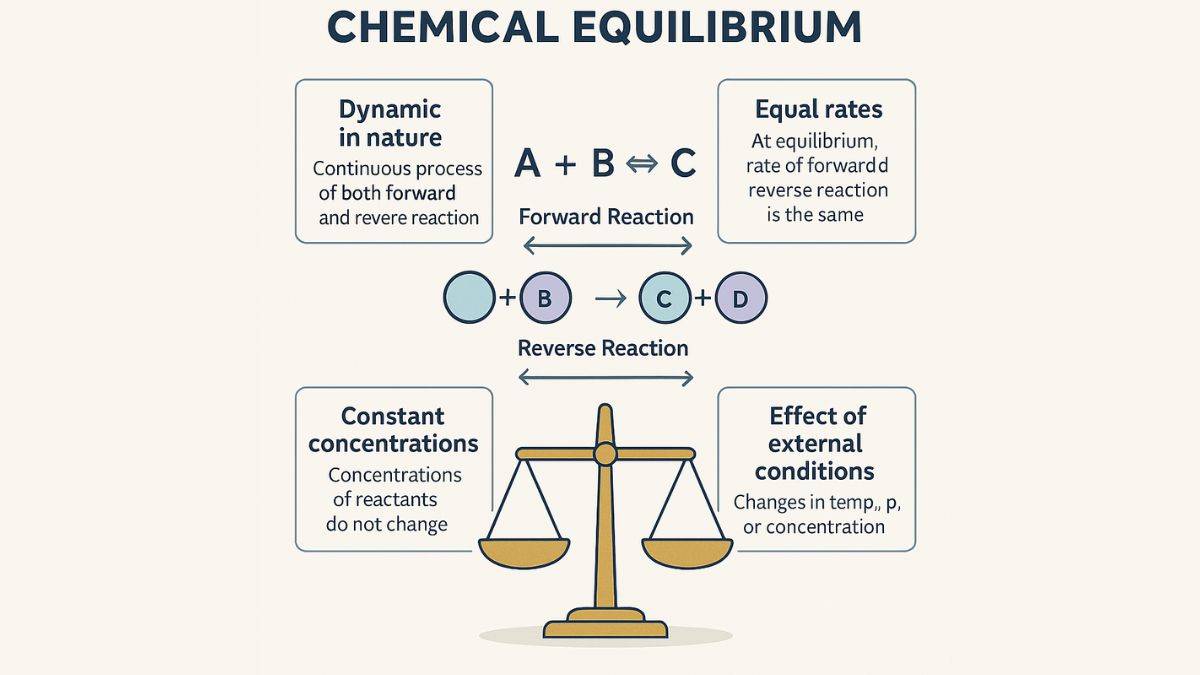
Equilibrium in chemical process is am important topic in Class 12 Chemistry. Chemical equilibrium is a state in chemical reaction where the rate of forward reaction and reverse reaction is same.
For example, if you mix lemon juice, sugar, and water in a big jar. Initially sugar is dissolved in water. Later you add more sugar in the water. Due to large amount of sugar is added, it will not dissolve in water. As time passes, some sugar dissolves and some crystallizes back out. At this is appoint where the rate of sugar dissolved is equal to the rate of sugar crystallizes. This is a chemical equilibrium.
This topic is also important from the exam point of view. Various entrance text like JEE Mains, NEET, etc. includes chemical equilibrium in their syllabus.
Also Check:
| NCERT Class 11 Notes | |
| Class 11 Chemistry NCERT notes |
- What is Chemical Equilibrium?
- Types of Chemical Equilibrium
- Factors Affecting Chemical Equilibrium
- Importance of Chemical Equilibrium
- Characteristics of chemical equilibrium
What is Chemical Equilibrium?
A state in a chemical reaction where the rate of the forward and reverse reaction is equal is called chemical equilibrium. At this point, the concentration of reactants and products remains constant over time.
Example:
Chemical Equilibrium Key Features
1. Equilibrium occurs in a reversible reaction.
2. The system seems to be stable, but the reaction continues at equal rates in both directions.
3. Equilibrium can be dynamic, which means the molecules are reacting, yet no overall changes are observed.
Important Links:
| NCERT Class 12 notes | |
| Class 12 Maths NCERT notes |
Types of Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium is a state where forward and reverse reactions are equal and the concentration of reactants and products is constant over time. Depending on the nature of substances involved and the phase of the system, types of chemical equilibrium are categorized.
Types of Chemical Equilibrium
1. Homogeneous Equilibrium: In the homogeneous equilibrium, all the reactants and products are usually in the same phase.
(Haber process).
2. Heterogeneous Equilibrium: In the heterogeneous equilibrium, both reactants and products are in different phases.
Factors Affecting Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium position can be affected by the change in external conditions such as temperature, volume, concentration, pressure, and catalyst. These changes are capable of shifting the balance toward either the reactants or the products. As per Le Chatelier's Principle, a system will adjust itself to counter any changes imposed on it.
Also Read: NCERT Solutions | Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
Factors Affecting Chemical Equilibrium
- Concentration: Adding reactants or products to the system will shift the equilibrium to reduce the change. Example: Adding a reactant shifts the equilibrium to form more products.
- Temperature: An Increase in temperature favours the endothermic direction, and a decrease in temperature favours the exothermic direction.
- Pressure (for gas): An Increase in pressure shifts the equilibrium towards fewer gas molecules, and a decrease in pressure shifts the equilibrium to more gas molecules.
- Catalyst: It speeds up the rate of forward and reverse reactions equally. The position of equilibrium is not shifted.
- Volume ( related to gases): A change in volume affects the pressure, which indirectly shifts the equilibrium depending on the number of molecules.
Importance of Chemical Equilibrium
Here we have mentioned a few points on the importance of chemical equilibrium.
1. Haber's Process: In this process, ammonia is prepared by combining nitrogen with hydrogen. At relatively low temperature, high pressure, and the presence of iron as a catalyst, the yield of ammonia is high.
2. Contact Process: In this process, oxidation of sulphur dioxide into sulphur trioxide is the fundamental reaction involving chemical equilibrium.
Characteristics of chemical equilibrium
The key characteristics of equilibrium in chemical processes are mentioned below:
1. It is dynamic in nature
2. The rate of forward and reverse reactions is equal.
3. The concentration of reactants and products remains constant over time.
4. Equilibrium occurs in a reversible reaction only.
5. Equilibrium is affected by external conditions such as temperature, concentration, or pressure.
Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Chemical Equilibrium
- Lewis Acids and Bases
- Precipitation Titration
- Arrhenius Acid
- Hydrocyanic Acid
- Equilibrium Processes
- Equilibrium in Chemical Processes
- Homogeneous Equilibria
- Heter Heterogeneous Equilibria
- Applications of Equilibrium Constant
- Factors Affecting Equilibria
- Ionic Equilibrium in Solution
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Ionization of Acids and Bases
- Solubility Equilibria of Sparingly Soluble Salts
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test