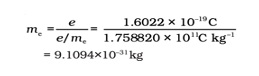- What are electrons?
- Discovery of an electron
- Charge on the electron
- Properties of Electrons
- Structure of Atom for Class 11
- Illustrated examples
- FAQs on What are Electron
What are electrons?
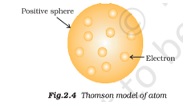
An electron is a negatively (-1) charged particle. The magnitude of protons and electrons is the same, but electrons contain an opposite sign. However, the molecular weight and size of electrons and protons differ from each other. That is why neutral atoms or compounds have an equal number of electron atoms and proton atoms/molecules. In physics, electrons play an essential role in concepts like electricity, thermal conductivity, magnetism, etc. This role can further be extended to electromagnetic and weak interactions.
Electrons have a circular field that surrounds the outside (outer surface) of an electron. If an electron is in a relative field to that of an observer, the person can observe the electron’s magnetic field.
Discovery of an electron
The electron was identified by the Physicist named J.J.Thompson with John S. Townsend and H.A.Wilson in 1897 while experimenting on cathode rays.
Charge on the electron
R.A.Millikan did the oil drop experiment to find out the charge on the electrons. He determined an equation on an electron’s charge, which is – 1.6 × 10–19 C. The current acceptable value is – 1.6022 × 10–19 C.
By combining this theory with J.J.Thompson, a mass of an electron was determined, which is shown below:
Properties of Electrons
- Electrons possess a negative charge.
- Within an atom, they form an outer shell and stay there in the magnetic field.
- The symbol of an electron is ‘e−’.
- The molecular mass of an electron is 1/2000 times compared with the mass of hydrogen tom.
- The nucleus has a positive charge in the outer shell.
- When compared to a proton, the molecular mass of an electron is 1/1837 times.
- The negative charge of an electron is equal to 1.602 × 10-19 coulomb in magnitude.
Structure of Atom for Class 11
For the year 2021, as per the new pattern, the chapter structure of atoms holds a weightage of 6 marks, including 3 questions (one short, one very short, and one objective type question).
Illustrated examples
1. Write the three electron rules used when assigning electrons to orbitals.
Answer: The rules used in assigning electrons to orbitals are as follows:
- The Aufbau principle
- The Pauli-Exclusion principle
- Hund’s Rule
2. Write the absolute charge of an electron.
Answer: The absolute charge of an electron is -1.6022 x 10^-31.
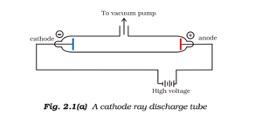
3. Illustrate the cathode rays with the help of a diagram.
Answer: Cathode ray tube is made up of electrodes, which are two thin pieces of metal. Through evacuation, the pressure of different gases can be increased or decreased as per the requirements. When sufficient force is passed through the electrodes, the current passes to the positive charge (anode) from the negative charge (cathode). The diagram of the cathode ray discharge tube is illustrated below -
FAQs on What are Electron
Q: What is the difference between neutrons and electrons?
Q: Do electrons repulse each other?
Q: What is the molecular mass of an electron as compared to a proton?
Q: Do electrons decay?
Q: How many 6p electrons are present in Be?
Chemistry Structure of Atom Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Isotope Meaning
- Mole Concept
- What are Electrons
- Isotopes and Isobars
- What is a Saturated solution
- Difference between Atom and Ion
- Discovery of Sub Atomic Particles
- Atomic Models
- Developments Leading to Bohr's Model of Atom
- Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
- Bohr's Model of Hydrogen Atom
- Towards Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
- Structure of Atom
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test