The Kössel-Lewis approach to chemical bonding is a foundational theory that explains how atoms achieve stability by attaining noble gas electron configurations through electron transfer or sharing. Proposed by Walther Kössel and Gilbert N. Lewis, it emphasizes the role of valence electrons in forming ionic and covalent bonds, with atoms striving to complete their octet (or duplet for hydrogen) to achieve minimum energy and maximum stability.
A chemical bond is the attractive force that holds atoms or ions together in a compound. Atoms bond to achieve greater stability, often by attaining a configuration similar to that of noble gases. The concept of chemical bonding is central to chemistry, as it explains how elements combine to form the vast array of substances we encounter.
In the early 20th century, two scientists—Walter Kossel and Gilbert N. Lewis—proposed pioneering theories to explain how atoms bond. Their ideas laid the groundwork for modern chemical bonding theory.
Aslo Check: NCERT Solutions
Kossel-Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding: As we know, matter is made up of more than one type of element. Except for noble gases, no other elements, under normal conditions, can exist alone in nature. They occur as a group of atoms, in the form of one species, with characteristic properties. Since a group of atoms cannot hold itself together, some force is holding them together. This ‘attractive force’, which is holding the elements – atoms, ions and so on together to form different chemical species, is called a chemical bond.
- Definition of Kossel-Lewis approach in Chemical Bonding
- Ionic Bond
- Octet Rule
- Covalent Bond
- Lewis Symbols
- Steps to draw a Lewis Structure
- Significance of Lewis Symbols
- Formal Charge
- Practice Questions
- Summary Table
- Related Study Materials for CBSE Class 11
- Complete Class 11 Chemistry Chapter-wise Notes
Definition of Kossel-Lewis approach in Chemical Bonding
The Kossel-Lewis approach in chemical bonding explains how atoms form chemical bonds to achieve stability by attaining a noble gas electron configuration (an octet). In 1916, Walter Kossel and Gilbert N.Lewis independently developed this approach.
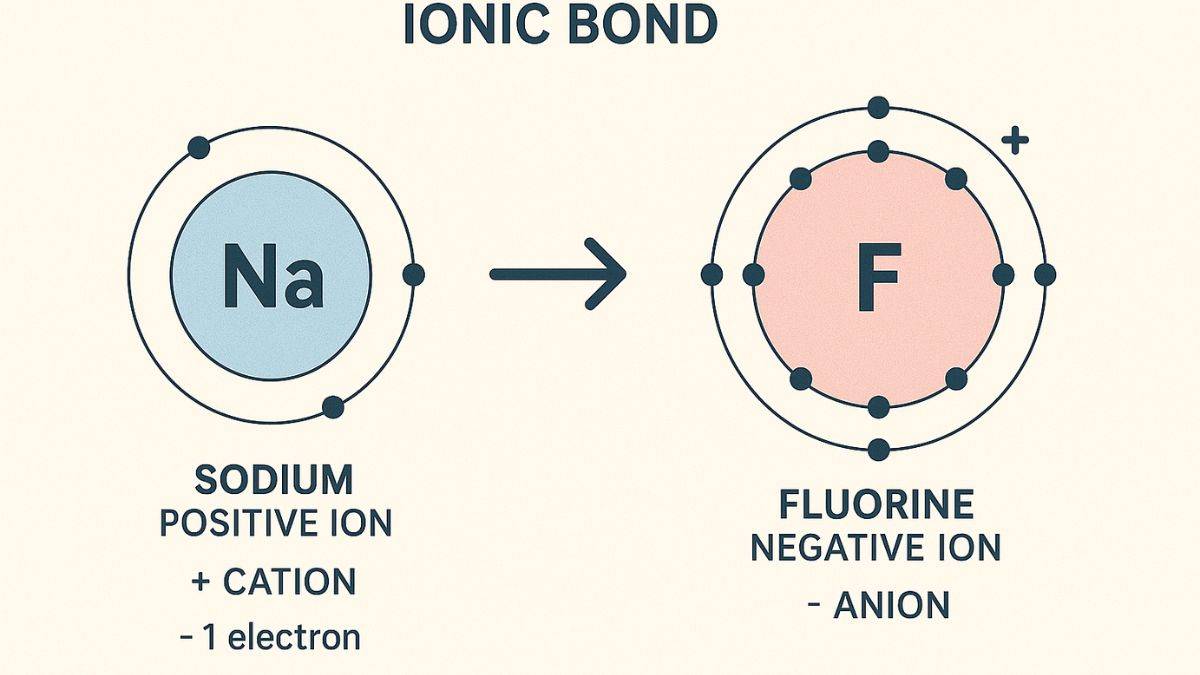
According to Walter Kossel, the atom of a metal and a non-metal can attain stability by transferring electrons, forming ionic bonds. On the other hand, Gilbert N.Lewis proposed that atoms can attain stability by sharing electrons.
Important Links:
| NCERT Class 11 Notes | |
| CBSE Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Notes |
Ionic Bond
The transfer of electrons from one atom to another leads to the formation of a chemical bond called an ionic bond. It forms between metal and non-metal.
Properties of Ionic Compounds Brittle
- Soluble in water
- Form crystalline solids
- High boiling and melting points
- Conduct electricity when soluble in water or in a molten state
Example of Ionic Compounds
- MgO (Magnesium oxide)
- KBr (Potassium bromide)
- NaCl (Sodium chloride – table salt)
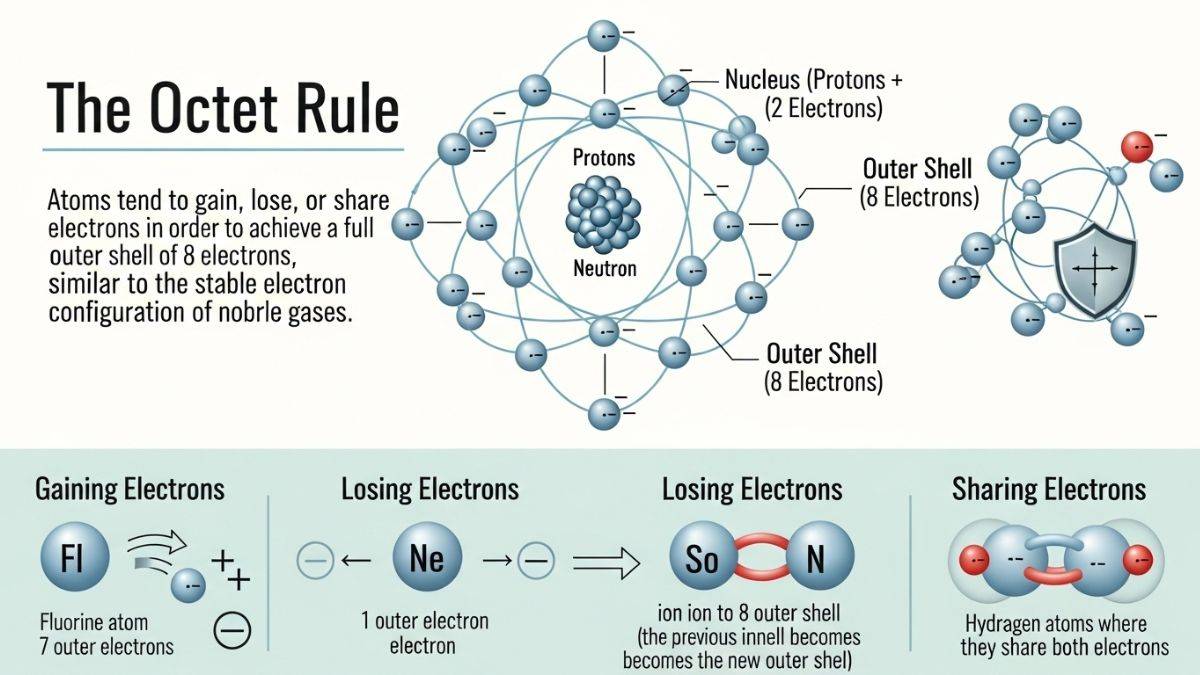
Octet Rule
In 1916, Kossel and Lewis developed the electronic theory of chemical bonding. According to the theory, atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons to have an octet in their valence shells. This is known as the octet rule.
Covalent Bond
A chemical bond formed by the sharing of an electron pair by two atoms is called a covalent bond. This bond occurs between non-metallic elements, which need electrons to complete their octet to become stable. With the help of covalent bonds, we can explain the structure of many important substances such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), oxygen (O₂), and water (H₂O).
Also Check: Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
How is a covalent bond formed?
In the formation of covalent bonds, atoms share electrons to attain a stable outer shell of electrons. The atoms mutually use the shared electrons to complete their valence shells.
Examples:
- H₂ (Hydrogen molecule): Each hydrogen shares one electron.
- O₂ (Oxygen molecule): Each oxygen shares two electrons (double bond).
- N₂ (Nitrogen molecule): Each nitrogen shares three electrons (triple bond).
Covalent bonds can be polar (unequal sharing) or non-polar (equal sharing), depending on the electronegativity difference between the atoms.
Polar Covalent Bond
The polar covalent bond form is defined as the bond in which the electrons are shared among the elements that have a difference of electronegativity between 0.5 and 2.0.
Dipole moment
The concept of dipole moment can be defined as the outcome of the magnitude of the charge on any of the atoms, along with the distance between them. It has been represented by the Greek letter ‘µ’ and has been expressed mathematically: µ = e × d Where, e refers to the charge on any one of the atoms determines the distance between the atoms. The unit of dipole system in the CGS system is the debye (D).
Lewis Symbols
A simple and effective way to represent the valence electrons (outermost electrons) of an atom is the Lewis symbol. They are also known as the Lewis dot symbol. These symbols were introduced by Gilbert N.Lewis to visualize the formation of chemical bonds by losing or gaining or sharing electrons.
Important Links:
| NCERT Class 12 Notes | |
| CBSE Class 12 Maths NCERT Solutions |
Structure of Lewis Symbol
The symbol consists of the chemical symbol of an element and a dot placed around the symbol to represent the valence electrons. Each dot represents a valence electron. The placement of the dot is on the four sides - top, bottom, left, and right of the symbol of the element.
For Example:
- Neon (Ne) → ··Ne·· (8 valence electrons – a complete octet)
- Oxygen (O) → ··O·· (6 valence electrons)
- Hydrogen (H) → H· (1 valence electron)
Key Component of a Lewis Structure
- Chemical symbols
- Dots represent non-bonding electrons (lone pairs).
- Lines represent shared electron pairs (covalent bonds).
Steps to draw a Lewis Structure
The steps to draw the Lewis structure are mentioned below:
- Calculate the total number of valence electrons for all atoms in molecules.
- The least electronegative atom (except hydrogen) is placed at the centre.
- Now connect the atoms using the single bonds (each bond uses two electrons).
- Distribute the remaining electrons as a lone pair.
- If the octet is not complete, make double or triple bonds.
- Check the formal charge for the stable structure.
Significance of Lewis Symbols
Lewis's symbol is used to represent the valence electrons of an atom. This symbol helps to explain how atoms bond with each other to form molecules and compounds. The Lewis symbol consists of an element's chemical symbol surrounded by dots. The dots represent the valence electrons. Below are the significances of the Lewis symbol.
- Helps in predicting atoms' bonding - whether they gain, lose, or share electrons.
- It is the starting point for constructing the Lewis dot structures.
- It explains the Octet Rule by displaying how atoms try to achieve stable electron configurations.
- It is a visual tool to understand the bonding of ionic and covalent compounds.
Formal Charge
Practice Questions
Summary Table
Related Study Materials for CBSE Class 11
Complete Class 11 Chemistry Chapter-wise Notes
Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics