Chemical bonding is a crucial concept to understand the structure and properties of matter. Also, it helps to explain how atoms combine to form molecules and compounds. The involvement of chemical compounds is not limited to our diets and medicines, but it has countless real-life applications. Knowledge of the topics such as covalent, metallic bonds, and ionic, will help students to know the behaviour of different materials, their ability to conduct electricity, or how they react with other substances. Students can build a strong foundation in chemistry and spark curiosity about the world at the atomic level by exploring the application of chemical bonding in industries, nature, and daily life.
Important links:
| NCERT Class 11 Notes | |
| CBSE Class 11 Chemistry NCERT notes |
- Define Chemical Bonding
- Types of Chemical Bonding
- Role of Chemical Bond in Molecular Structure and Geometry
- Application of Chemical Bonding
- Related Study Materials for CBSE Class 11
- Complete Class 11 Chemistry Chapter-wise Notes
Define Chemical Bonding
The force of attraction that holds various constituents (atoms or ions) together in different molecules or compounds is called chemical bonding. This occurs when atoms lose, gain, or share electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration.
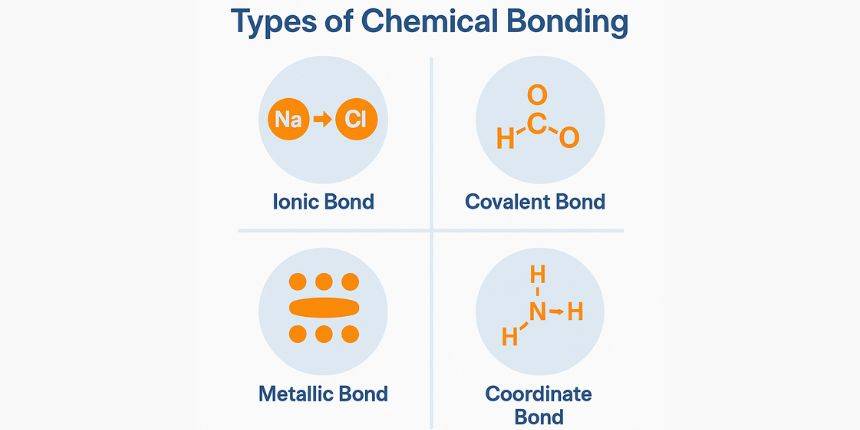
There are mainly three types of chemical bonds:
- Ionic Bond
- Covalent Bond
- Metallic Bond
Also Read:
| CBSE Class 12 NCERT notes | |
| Class 12 Maths NCERT notes |
Types of Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding is classified into three main types based on how atoms achieve stability. Below are the types of chemical bonds.
Types of Chemical Bonding
- Ionic Bonding:
- It is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another between a metal and a non-metal. Ionic compound conducts electricity when dissolved in water; they are crystalline solids and have high melting and boiling points. The example of an ionic compound is Sodium chloride (NaCl).
Important Link: NCERT Solutions
- Covalent Bonding:
- When atoms share electrons between non-metals, covalent bonding is formed. Based on the number of electron pairs shared, a covalent bond can be single, double, triple, polar, non-polar, or dative bond.
- Covalent compounds can be polar or non-polar, have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds, and have poor electrical conductivity. Examples of covalent compounds are Water (H₂O) and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
- Metallic Bonding: Involves a sea of delocalized valence electrons that can move freely through the structure. It occurs between metal atoms. Metallic bonding has a lustrous appearance; they are malleable and ductile. Also, they have good electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Hydrogen Bonding: It is a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction bonded to a highly electronegative atom (like O, N, F). Hydrogen bonding can affect the boiling and melting points. Also, they are important in biological molecules (DNA, proteins).
Role of Chemical Bond in Molecular Structure and Geometry
It's through chemical bonds that we get to learning the ins and outs of the geometry and structure of molecules. Now, molecular geometry and molecular structure are two different concepts, and we do not use them interchangeably.
Role of Chemical Bond in Molecular Structure
The molecular structure of chemical bonds tells us all about the fine details of how strongly or weakly the bonds are attached to each other in their atomic and ionic arrangements. That shows how electrons are distributed in a molecule. This also provides us with the three-dimensional geometry of the molecule. All these aspects influence the physical and chemical properties.
Role of Covalent Compounds
Electron pairs exist for stability in the configuration of atoms in molecules. VSEPR theory determines their arrangement by predicting molecular shapes through the repulsions that arise because of electron pairs. The shapes change because of that. H2O has a bent shape, while CH4 has a tetrahedral one.
Role of Ionic Compounds
Molecules also have ions with positive and negative charges. The electrostatic forces need to be strong to hold these ions together. And these ions form a 3D lattice in the crystalline form.
Role of Metallic Compounds
The atoms in metallic compounds are attached closely to each other in a structural form. The shapes are like cubes and hexagons. Properties such as how malleable the atoms are and whether they can conduct electricity are understood through this.
Role of Chemical Bond in Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. It depends on the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom, as explained by the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory. The repulsion between these electron pairs determines the shape of the molecule.
Some popular examples of molecular geometries that should help in memorising would be
- Linear Geometry - CO2
- Tetrahedral Geometry - CH4
- Trigonal Bipyramidal Geometry - PCL5
- Octahedral Geometry - SF6
- Bent/Angular Geometry - H20
Role of Bond Angles and Molecular Polarity
All we should know at this stage is that polarity comes from the fact that when electrons are shared in covalent bonds, that would be an unequal distribution. This polarity will create dipole moments. The molecular polarity gives rise to physical properties, when it comes to boiling point and solubility, as well as reactivity.
Role of Van der Waals Forces
Beyond the covalent and ionic bonding roles, we need to know when intermolecular forces are weaker. This is because not all atoms and molecules have strong forces at all times. There could be certain temporary situations when the forces between molecules are too weak or dipoles are formed temporarily. You can take the simple example of gases, where the weaker type of forces is termed van der Waals forces.
Application of Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding has several important uses in the real world.
Material Science and Engineering
As chemistry students, we can easily identify properties of different substances, including metals, plastics, and ceramics, based on the bonding structure. For instance, we can say that metallic bonds determine if a substance has electrical conductivity. In the same manner, engineers can design materials that resist heat by learning which substances have covalent and ionic bonds.
Agricultural Products
For fertilisers, chemists need to know about specific ways of bonding chemicals to create compounds that enable the right nutrients can be released to plants perfectly. They also need to see whether the plant is able to absorb them for healthier growth.
Related Study Materials for CBSE Class 11
Here, we have provided links to the Class 11 study material.
Complete Class 11 Chemistry Chapter-wise Notes
Students can find the complete notes for Class 11 Chemistry as per the NCERT solutions here. Below are the links:
Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics