Every chemical compound is made up of atoms. Two or more atoms come together to form a molecule of a chemical compound. These molecules form due to a chemical bond between the two atoms. Class 11 Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure chapter discusses several types of chemical bonds, including ionic or electrovalent bond, covalent bond, metallic bond, and hydrogen bond. We have covered all these topics in the NCERT Notes provided by Shiksha.
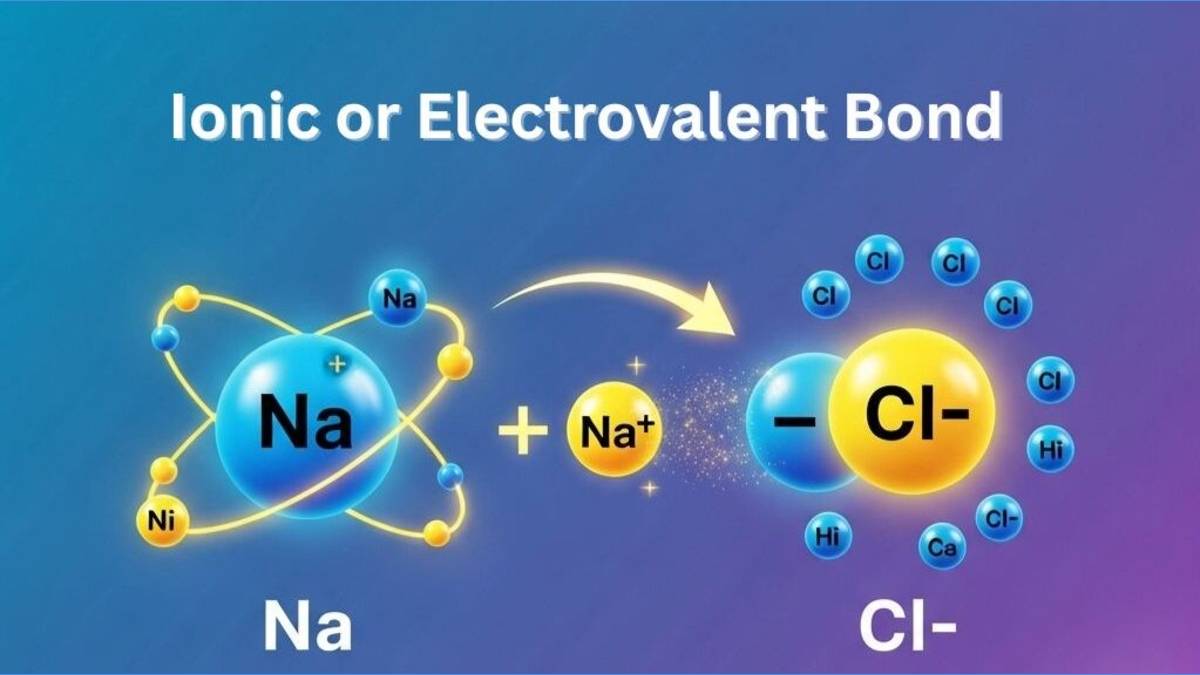
This article deals with the ionic bond and its important details. We'll discuss its formation, properties, conditions, and many more exciting concepts related to the electrovalent bonds. These electrovalent bonds are a result of the complete transfer of valence electrons present on the outer shell (orbit) from one atom to another. It creates two oppositely charged atoms, which we call ions. The electrostatic forces between positively charged cations and negatively charged anions hold ions together.
We will discuss the formation of a stable ionic compound, its properties. For a deep understanding of the difference between a covalent bond and an ionic bond, you must know the electronic configuration of the elements.
You can download the short revision PDF related to this topic below. For complete information about concepts, applications, compounds, etc, read the article.
- What is Electrovalent Bond (Ionic bond) ?
- Ionic Bond NCERT Definition
- Formation of Electrovalent Bond
- Conditions of Ionic Bond Formation
- Properties of Ionic Bond
- Factors Influencing Electrovalent Bond Strength
- Born-Haber Cycle and Energetics
- Applications and Importance of Ionic Bonds
- Examples of Ionic Compounds
- What is Covalent Bond?
- Difference Between Covalent and Ionic Bond
- Electrovalent Bond - Important Points to Remember
- Complete Class 11 Study Material
What is Electrovalent Bond (Ionic bond) ?
Electrovalent bonds are chemical bonds formed due to the presence of two oppositedly charged ions. When any atom loses its free electron (generally of the outermost shell) to the nearby atom, both atom becomes oppositedly and equally charged ions. The positive charged ion is named as cation and the negatively charged ion is named as anion.
Both cation and anion exert equal and opposite amount of electrostatic force of attraction. This force of attraction holds these two ions together, resulting in a chemical compound molecule. Thus formed chemical bond due to electrostatic attraction is called electrovalent bond.
As per the NCERT textbooks." Most ionic compounds have cations derived from metallic elements and anions from non-metallic elements. The ammonium ion, NH4+ (made up of two non-metallic elements) is an exception. It forms the cation of a number of ionic compounds."
This type of bond typically occurs between metals and non-metals due to their differing electronegativities, enabling the metal to lose electrons and the non-metal to gain them, achieving stable electron configurations akin to noble gases.
Ionic Bond NCERT Definition
As per NCERT Definition "The bond formed by the complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another, generally from a metal to a non-metal, to form cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces."
The NCERT Definition discusses three important points:
- Transfer of electrons from one atome to another
- Transfer of elctrons from metal to non-metal
- Electrostatic force of attraction
The above three points are immensely important for understanding the concept of the electrovalent bonds. Exams like JEE require deep understanding of ionic bond formation. JEE Mains may explore behind-the-curtain concepts asking about the lattice energy of two compounds. Electrovalent bonds are only formed during the lattice formation exceeds the ionization energy. For example, the Electrovalent bond in NaCl is formed due to the same lattice energy compensation process.
JEE Twist: Why do certain ionic compounds like CsF have higher lattice energy than NaCl ?
The has a smaller ionic radius compared to . The smaller the ionic radius, the stronger the electrostatic force will be as electrostatic forces are inversely proportional to the square of the distance. The stronger electrostatic interactions results in higher energy as lattice energy is inversely proportional to the inter-ionic distance ( ).
Read More:
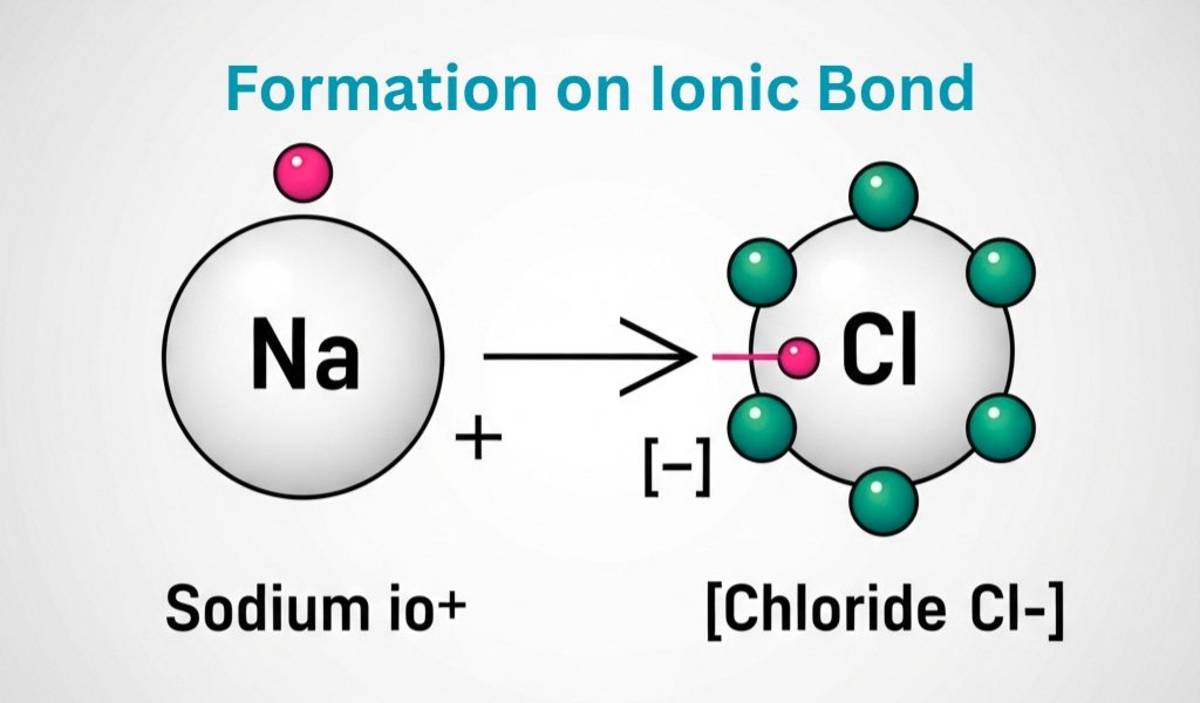
Formation of Electrovalent Bond
Ionic bond formation is basically based on energy transfer and electron transfer of constituent atoms. Check the step-wise process of ionic bond formation below.
- A metal which have low ionization energy loses electrons to form a cation: (For ex., Na → Na⁺ + e⁻, Na loses an electron due to low ionization energy).
- The non-metal which have electron affinity gains an electron to form an anion: (For ex., Cl + e⁻ → Cl⁻, Cl gains an electron due to electron affinity).
- Cation and Anion bonds together through electrostatic energy of attraction: (For ex., Na⁺ + Cl⁻ → NaCl, the ionic bonds get formed due to electrostatic force).
- During the formation huge amount of energy is released during lattice formation of crystalline structure, which is called lattice energy.
Conditions of Ionic Bond Formation
All metal and non-metals can not form a electrovaent bond, this is due to specific condition required to form a ionic bond. Read these conditions required for ioinc bond.
- There should be high difference in Electronegativity (greater than 1.7). Large electronegativity difference makes transfer of electrons easy. (For Ex. Na : 0.9, Cl : 3.0, difference = 2.1).
- Metals with low ionization energy have hgher chances of losing electron, resulting in cation.
- It is very favourable condition that the non-metal included in the process have high electron affinity. High electron affinity helps non-metal gain electron easily.
- For more stable chemical compound, the metal ion should be small with higher charge so that cystal can have high lattice energy.
JEE Students should also explore the application of Fajans' rules to predict partial covalent character in ionic compounds. This concept is frequently asked in the exams such as AlCl₃.
Properties of Ionic Bond
There are specific chemical characteristics in the Ionic compounds. Students must have complete information about the properties of the ionic bond. Read below;
- Electrovalent bonds are the strongest bonds among all chemical bonds, due to its electrostatic origin.
- Since ionic bonds area result of strong electrostatic attraction, they need higher energy to change bond strength. Due to this, they have high melting and boiling points (NaCl melts at ).
- Ionic Compounds are soluble in polar solvents. In the polar solvents, ions of the compound and solvent interact easily due to their similar nature, resulting in solubility.
- These Compounds are insoluble in nonpolar solvents like hexane due to their non-electronic nature, due to electrovalent bonding.
- Ionic compounds can conduct electricity in liquid and gaseous form but not in solid form.
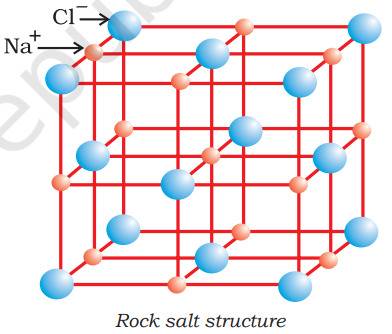
- These compounds form a high lattice energy crystalline structure, which is highly ordered such as NaCl has a cubic rock-salt structure.
Factors Influencing Electrovalent Bond Strength
There are several factors which decides the strength of the ionic bond formed. These facts are directly asked in many exams including CBSE class 12 Boards and others. You can read the factors below;
- ✔Ionic Charge = The larger the charge, the stronger electrostatic attraction will be. Stronger electrostatic attraction means stronger ionic bond.
- ✔Ionic Size= The smaller size reduces the distance between ions, resulting stronger electrostatic force. This will result in stronger ioinc bond, and higher lattice energy.
- ✔Lattice Energy = higher lattice energy ensures the stability of the compound.
JEE Main questions focuses on comparing melting points of two ionic compounds. For example MgO and NaCl . MgO has a higher melting point due to the higher charges and smaller ionic radii, resulting in greater lattice energy.
Born-Haber Cycle and Energetics
The Born-Haber cycle quantifies the energy changes in ionic bond formation. For NaCl, it includes:
Sublimation:
⇓
Ionization:
⇓
Dissociation:
⇓
Electron Gain:
⇓
Lattice Formation:
There is a release of lattice energy, which partially gets absorbed in electron transfer and the rest in the surroundings.
The net reaction is exothermic if lattice energy outweighs the endothermic steps.
Read more:
Applications and Importance of Ionic Bonds
Examples of Ionic Compounds
What is Covalent Bond?
Difference Between Covalent and Ionic Bond
Electrovalent Bond - Important Points to Remember
Complete Class 11 Study Material
Commonly asked questions
Why does MgO have a higher melting point than NaCl ?
Higher melting point means more energy is required to break the ionic bond. Since the ionic bonds in MgO are stronger than in NaCl due to various reasons, It have higher melting and even boiling point. Reasons are listed below:
- In MgO, Magnesium and oxygen ions carry a +2 and -2 charge while sodium and in NaCl, chlorine ions carry a +1 and -1 charge. Due to higher charges more electrostatic attraction is involved.
- The smaller ionic radius of Mg2+ are smaller compared to Na+, makes the bond stronger in MgO.
- Due to larger elctrostatic force and smaller ionic radius, ionic bond in MgO are stronger, resulting in higher lattice energy.
- The stronger ionic bonds in MgO needs more heat to break the lattice structure, specifies a higher melting point.
What are the differences between covalent and ionic bonding?
Covalent and electrovalent bonding are the two major chemical bonding processes. These two bonds are different from each other in multiple aspects. Check the table below to know a concise summary of the differences.
| Particular | Covalent Bond | Ionic Bond |
| Formation | Due to the complete transfer of electrons | Due to the sharing of electron pairs |
| Ion formation | No ions formed | Cations and Anions formed. |
| Nature | Electrostatic attraction between ions | Electrostatic attraction between nuclei and shared electrons |
| Strength | Strong | Less strong |
| Melting/Boiling point | High due to a strong bond | lower due to weaker bond |
| Polarity | Highley Polar | Non-Polar |
What are the factors favourable for the formation of the Ionic Bonds?
As you know, electrovalent bonds result very strong electrostatic attraction force. All the factors that help maximize this electrostatic attraction are important for the formation of the ionic bond. Here are the important factors;
- Low ionization energy Metal
- High electron affinity Non Metal
- Large-sized cations
- Small-sized anions
- Electronegativity equal to or greater than 1.7
Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics