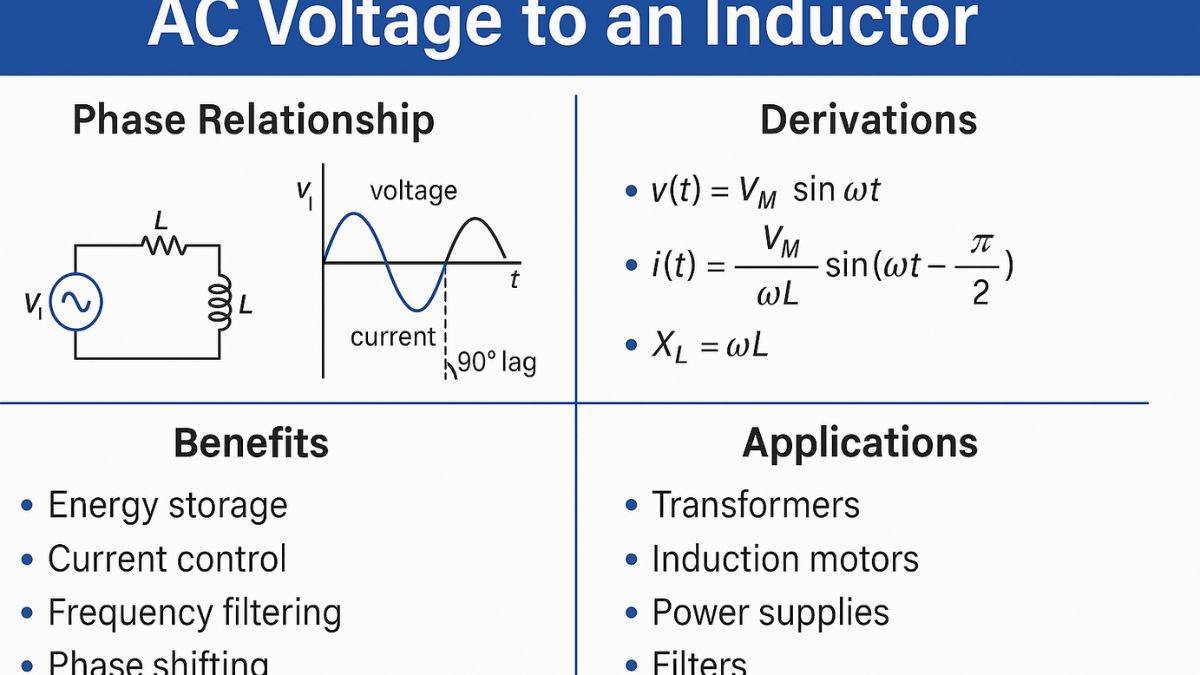
An inductor is a device that stores energy in its magnetic field. When AC voltage is applied to an inductor, it resists a small change in current and creates a phase difference between voltage and current. Phase difference is the angular difference between the phasors of voltage and current.
It is used in numerous devices like motors, filters, chokes, and transformers. Students can explore the article for theory, mathematical derivation, benefits, and real-world application of applying AC voltage to an inductor.
Important Links:
| NCERT Class 12 notes | |
| CBSE Class 12 Maths NCERT notes |
- What happens when AC Voltage is applied to an Inductor?
- Benefits of Applying AC Voltage to an Inductor
- Power in an Inductive AC Circuit
- NCERT Physics Class 12 Chapters
- Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions
- Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
What happens when AC Voltage is applied to an Inductor?
When AC voltage is applied to an ideal inductor, it generates a self-induced EMF (electromotive force), due to Lenz's Law. This led to the current lagging the voltage by 90 degrees (π/2 radians).
Mathematical Derivation
Here we will derive the current response when an AC voltage is applied to an inductor.
- AC voltage:
- peak voltage
- is angular frequency
- Inductance of the coil
Using the inductor voltage-current relationship:
Voltage expression:
Integrating both sides:
Let for simplicity:
Conclusion:
Current lag the voltage by 90°, and the amplitude is:
Impedance of an Inductor
In the frequency domain, the inductor’s impedance is:
- : Imaginary unit (phase shift)
- : Inductive reactance, measured in ohms (Ω)
Benefits of Applying AC Voltage to an Inductor
Benefits of applying AC Voltage to an Inductor
- An inductor stores the energy in a magnetic field. These energy are used for power supply and smoothing circuits.
- Inductor block high frequency and allow the low-frequency signals to pass. Due to this behavior of inductor it is used in audio and radio circuit to filter signals.
- Inductors cause the current to lag the voltage, which helps to create a phase shift in AC circuits for motors and oscillators.
- The key components in a transformer are the inductor. It is essential to change the voltage level in AC transmission.
Also Read:
| NCERT Class 11 Notes | |
| Class 11 Chemistry NCERT notes |
Power in an Inductive AC Circuit
In a pure inductor:
- Average power (P) = 0.
- Because the power alternates between positive and negative due to a phase difference (90°).
- There is no loss of energy by its return to the source in each cycle.
This led to the concept of reactive power (Q), measured in volt-ampere reactive.
Important Link: NCERT Solutions
NCERT Physics Class 12 Chapters
Here we have provided the link for the Class 12 Physics NCERT notes.
| Sl. No |
Name of Chapter |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields |
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
Chapter 13: Nuclei |
| 14 |
Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits |
Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions
Students can find here the NCERT solutions for Physics Class 12. It will be helpful in exam preparation.
| Sl. No |
Name of Chapter |
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits |
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
Here we have provided the FAQs based on the topic: AC voltage applied to an inductor.
Commonly asked questions
What happens when a voltage is applied across an inductor?
The inductor generates induced electromotive force (EMF) and opposes the changes in the current flow. Due to this the current lag the voltage by 90 degrees.
When AC voltage is applied to an inductor, current lags behind voltage by angle of?
The current lags the voltage by an angle of 90 Degree (? /2 radians). This is due to the inductor opposing the change in current.
Physics Alternating Current Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Coulomb's Law
- Power in AC Circuit
- Representation of AC Current and Voltage by Vector
- AC Voltage applied to a Series LCR circuit
- AC Voltage applied to a Capacitor
- AC Voltage Applied to an Inductor
- AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor
- Alternating Current Overview
- Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
- Temperature Dependence of Resistivity
- Potentiometer
- Application of Gauss's law
- Electric Dipole
- Electric Flux
- Gauss Law
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test