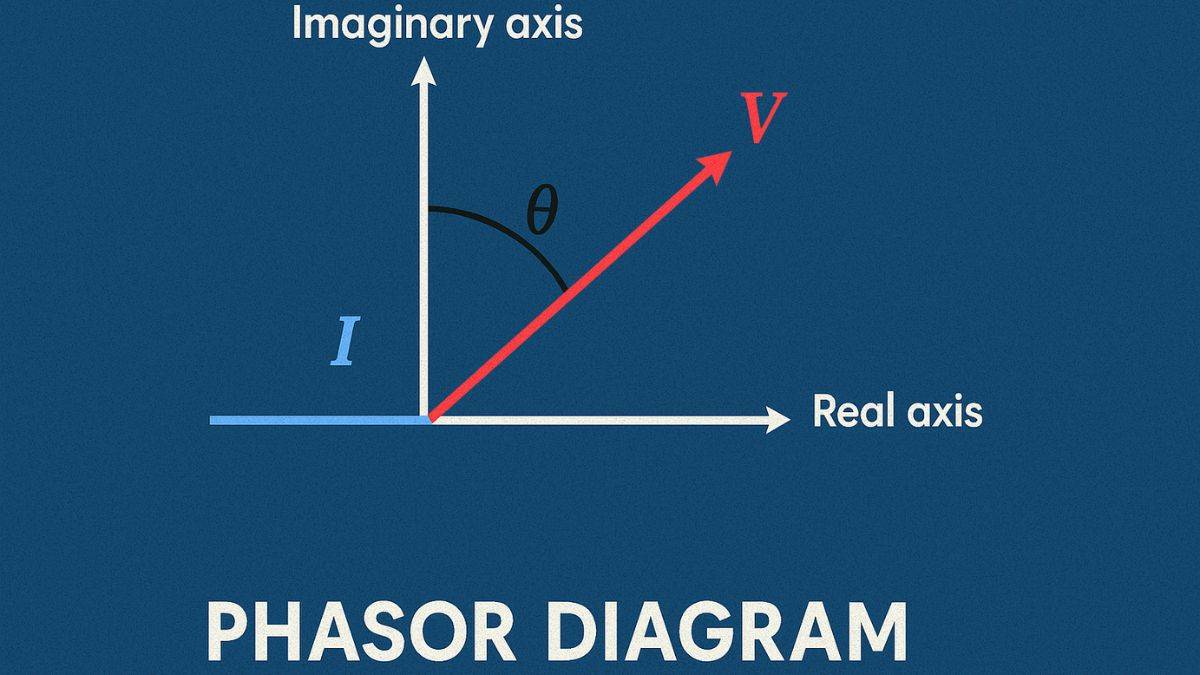
Representation of AC and voltage by vector is an important concept in Physics. We know that the current and voltage change their magnitude and direction with time. This relationship between current and voltage is explained with the help of a simpler method of representation called the vector (or phasor) method. Check the article to understand the topic "representation of AC current and voltage by vector" in detail..
Important Links:
| NCERT Class 12 notes | |
| Class 12 Maths NCERT notes |
- What is a Phasor?
- How does Phasor Represent AC Signals?
- Why use Phasor?
- Phasor Representation of Voltage and Current
- Application of Phasor Representation
- Class 12 Physics NCERT Notes
- Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions
What is a Phasor?
A phasor is a vector quantity that is used to represent the relationship between the current and voltage. In an AC circuit, current and voltage change their magnitude and direction. Instead of showing this change using a sine wave, we represent it by rotating an arrow (vector) called a phasor.
The length of the phasor represents the peak value of voltage or current in the AC circuit. Phasor rotates counterclockwise with an angular velocity (ω) same as the frequency of the AC signal.
Read More: NCERT Solutions
How does Phasor Represent AC Signals?
The vertical components of the rotating phasor onto the y-axis are the instantaneous value of the AC signal. The vertical projection traces out a sine wave as the phasor rotates.
V(t)=Vm sin(ωt+ϕ)
Where,
- Vm is peak voltage (length of phasor)
- ω is the angular frequency (speed of rotation)
- (ωt+ϕ) angle of phasor
- ϕ initial angle or phase angle
Why use Phasor?
Phasors are useful in calculating difficult AC circuit problems using algebra rather than calculus. This is useful to calculate the phase relationship in an AC circuit. By identifying phase relationships, a phasor can be visualized geometrically.
Phasor Representation of Voltage and Current
Consider an AC circuit with an inductor (L), a capacitor (C), and a resistance (R).
- Pure Resistor: V and I are in the same phase. The phasor of voltage and current lies in the same line.
- Pure Inductor: Current (I) lags voltage by 90°. We draw the current phasor 90° behind the voltage phasor.
- Pure Capacitor: I leads V by 90°. The current phasor is drawn 90° ahead of the voltage phasor.
Important Links:
| NCERT Class 11notes | |
| NCERT Class 11 Chemistry |
Application of Phasor Representation
Below is the application of phasor representation.
- Signal processing
- Electronics and communication engineering
- Power calculation in AC systems
- Electric machines and transformers
- AC circuit analysis
Class 12 Physics NCERT Notes
Students can find here the link for all chapters in Class 12 Physics.
| Sl. No |
Name of Chapter |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields |
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
Chapter 13: Nuclei |
| 14 |
Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits |
Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions
Here we have provided Class 12 Physics NCERT solutions to help students prepare for the exam.
| Sl. No |
Name of Chapter |
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits |
Physics Alternating Current Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Coulomb's Law
- Power in AC Circuit
- Representation of AC Current and Voltage by Vector
- AC Voltage applied to a Series LCR circuit
- AC Voltage applied to a Capacitor
- AC Voltage Applied to an Inductor
- AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor
- Alternating Current Overview
- Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
- Temperature Dependence of Resistivity
- Potentiometer
- Application of Gauss's law
- Electric Dipole
- Electric Flux
- Gauss Law
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test