Thermodynamic processes describe how systems change their state variables, such as pressure, volume, and temperature. A single state variable can alter the system's nature and lead to a change in energy. This change affects the state in various ways, resulting in different types of thermodynamic processes, including isothermal, adiabatic, and isobaric.
If you are solving the NCERT Solutions for Thermodynamics or planning to sit for competitive exams, brush up quickly with this guide to thermodynamic processes. We outline the six major types of thermodynamic processes, their characteristics, and provide all the necessary information to understand the concepts clearly.
- What are Thermodynamic Processes?
- Why Learn Thermodynamic Processes for Competitive Exams
- Types of Thermodynamic Processes with NCERT Definitions
- Key Characteristics of Thermodynamic Process
- First Law Applications of Thermodynamic Process
- Real World Applications of Thermodynamics Process
- Conceptual Examples
- Key Points for JEE Main
What are Thermodynamic Processes?
A thermodynamic process is a change in a system's state. We characterise this change through variations in macroscopic variables, such as pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T).
You can learn more about thermodynamic state variables and equation state, for a better understanding.
Thermodynamic processes are the basis for the interconversion of heat and other forms of energy. They show us how systems absorb heat and perform work.
Additionally, to understand thermodynamic processes, we must learn about equilibrium conditions. These conditions define the stable states of a system, between which thermodynamic processes occur. That leads to two characteristics of thermodynamic processes: reversible and irreversible. (These are essential to learn when studying the Second Law of Thermodynamics.)
Why Learn Thermodynamic Processes for Competitive Exams
Thermodynamic processes and this chapter, as a whole, are part of the syllabus for several entrance exams after your CBSE board exam. You can check out some of these below.
- IISER Aptitude Test Physics Syllabus covers thermodynamic processes and their applications.
- If you are giving a thought to pursuing bachelor’s in science from any college in India, thermodynamics, with its laws and processes forms an important branch of physics in higher studies.
- Even the CUET PG Physics Syllabus requires knowledge of various types of processes, such as isothermal or adiabatic. So when preparing, you can always refer to the concepts explained in detail here.
Types of Thermodynamic Processes with NCERT Definitions
As we’ve seen, thermodynamic processes involve changes in the state variables. Now, which variable is kept constant under specific conditions can lead to different types of thermodynamic processes.
- Quasi Static Process: NCERT describes the behaviour of a quasi-static process as “In a quasi-static process, at every stage, the difference in the pressure of the system and the external pressure is infinitesimally small. The same is true of the temperature difference between the system and its surroundings.”
- Isothermal Process: Temperature remains constant ( constant). For an ideal gas, constant (Boyle's Law). According to NCERT, the definition is: “A process in which the temperature of the system is kept fixed throughout is called an isothermal process.”
- Adiabatic Process: No heat is exchanged . For an ideal gas, , where . NCERT mentions, “if the system is insulated from the surroundings and no heat flows between the system and the surroundings, the process is adiabatic.” See how adiabatic walls are used to allow two systems to reach thermal equilibrium.
- Isobaric Process: Pressure remains constant ( constant). Volume and temperature change proportionally.
- Isochoric Process: Volume remains constant ( constant). No work is done . Additionally, you may want to learn more about work in physics. NCERT says, “In an isochoric process, V is constant. No work is done on or by the gas.”
- Cyclic Process: System returns to its initial state, with no net change in internal energy
Further, NCERT differentiates the isobaric and isochoric processes in the following way -
“In isobaric processes the pressure is constant while in isochoric processes the volume is constant.”
Key Characteristics of Thermodynamic Process
1. Isothermal: Work done, , equals heat absorbed , as for an ideal gas.
2. Adiabatic: Work done, , reduces internal energy, lowering temperature.
3. Isobaric: Work done, . Heat changes internal energy and does work.
4. Isochoric: All heat increases internal energy ( ), as no work is done.
5. Cyclic: Total heat absorbed equals work done , as .
First Law Applications of Thermodynamic Process
Here is a simple way to learn how the first law of thermodynamics is derived for thermodynamic processes.
Meanwhile, you can check out our explanation of the 1st Law of Thermodynamics equation.
The First Law, , governs all processes:
Isothermal: , so .
Adiabatic: , so .
Isobaric/Isochoric: splits between and .
Cyclic: , so .
Real World Applications of Thermodynamics Process
Here are some popular applications of thermodynamic processes.
- Heat Engines: Cyclic processes convert heat to work, using isothermal and adiabatic steps (e.g., Carnot cycle).
- Refrigeration: Adiabatic expansion cools the refrigerant, while isothermal processes absorb heat.
- Natural Systems: Atmospheric processes (e.g., cloud formation) involve isobaric and adiabatic changes.
Use this table to remember each of the thermodynamic processes quickly.
| Type of processes |
Feature |
| Isothermal |
Temperature constant |
| Isobaric |
Pressure constant |
| Isochoric |
Volume constant |
| Adiabatic |
No heat flow between the system and the surroundings |
Conceptual Examples
To dig a little deeper, have a look at some examples of the major thermodynamic processes.
1. Isothermal: A gas in a metallic cylinder in a large reservoir expands slowly, maintaining constant temperature, absorbing heat to do work.
2. Adiabatic: A gas in an insulated container expands, doing work and cooling, as no heat is exchanged.
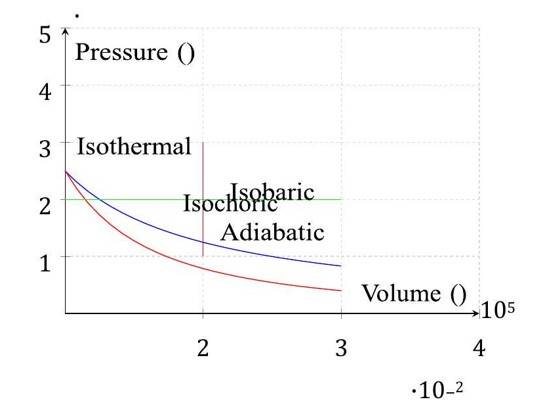
Check the diagram of thermodynamic processes for 1 mol of an ideal gas: isothermal ( ), adiabatic ( ), isobaric ( ), and isochoric ( ).
3. Isobaric: Heating a gas at constant pressure causes volume expansion, with heat increasing both internal energy and work.
4. Isochoric: Heating a gas in a rigid container increases temperature and internal energy, with no work done.
Key Points for JEE Main
Physics Thermodynamics Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- What is Internal Energy
- Thermodynamic State Variables Equation of State
- Thermodynamic Process
- Thermal Equilibrium
- Reversible and Irreversible Process
- Overview
- Uses of Colorimeter
- Specific Heat Capacity
- Specific Heat
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Law of Conservation of Energy
- Van Der Waals Equation
- Third law of thermodynamics
- Boltzmann Equation
- Helmholtz Equation
Other Class 11th Physics Chapters
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
- NCERT Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Notes
- Physics Motion in Plane
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Physics Motion in Straight Line
- Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Physics Oscillations
- Physics Waves
- Physics Thermal Properties of Matter
- Physics Motion
- Physics Gravitation
- Physics Thermodynamics
- Physics Work, Energy and Power
- Physics Units and Measurement
- Physics Laws of Motion
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test