NEET Biology Syllabus 2026 has been released by the NTA. Candidates preparing for exam must cover the NEET syllabus Biology 2026. The syllabus includes chapters from Botany and Zoology. Check below the NEET Biology chapter-wise weightage and download the syllabus PDF.
The NTA has released the NEET 2026 syllabus for Biology. The syllabus remains the same as last year. The Biology section of NEET exam is of the highest weightage, with the most number of questions (90 MCQs). The NEET Biology section is segregated into Botany and Zoology, and each of these sections contain 45 questions. Candidates need to prepare the Biology section in detail by covering all the topics prescribed by the NTA. The total Biology chapters for NEET 2026 are 10. Check below the detailed NEET Biology syllabus 2026 along with the chapter-wise weightage. Candidates can refer to this article to learn how to prepare for the Biology section of the NEET exam.
- NEET 2026 Biology Syllabus Overview
- NEET Biology Syllabus 2026
- NEET Syllabus Biology 2026 for Botany & Zoology
- NEET Biology Chapter Wise Weightage 2026
- List of Deleted Chapters of NEET Biology Syllabus
- Best Books to Prepare for NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus 2026 Analysis
- How to Prepare for NEET Biology 2026?
NEET 2026 Biology Syllabus Overview
Although there is no segregation of syllabus for Class 11 and Class 12, for the convenience of students, the table below brings the total chapters in Biology Class 11 and 12 for NEET 2026.
| NEET Biology Syllabus for Class 11 |
NEET Biology Syllabus for Class 12 |
|---|---|
| Diversity in Living World |
Reproduction |
| Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants |
Genetics and Evolution |
| Cell Structure and Function |
Biology and Human Welfare |
| Plant Physiology |
Biotechnology and Its Applications |
| Ecology and Environment |
Commonly asked questions
The NEET syllabus 2026 has been released by the NTA and NMC for Physics, Chemistry and Biology. Here is the syllabus for NEET UG 2026 exam below-
Physics | Chemistry | Biology |
|---|---|---|
Physics and Measurement | Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Diversity of Living Organisms |
Kinematics | Structure of Atom | Structural Organization in Plants & Animals |
Laws of Motion | Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Cell Structure and Function |
Work, Energy, and Power | Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Plant Physiology |
Rotational Motion | States of Matter: Gases and Liquids | Human Physiology |
Gravitation | Thermodynamics | Reproduction |
Properties of Solids and Liquids | Equilibrium | Genetics & Evolution |
Thermodynamics | Redox Reactions | Biology and Human Welfare |
Kinetic Theory of Gases | Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Biotechnology and its Applications |
Oscillation and Waves | P-Block Elements | Ecology and Environment |
Electrostatics | D- and F-Block Elements |
|
Current Electricity | Coordination Compounds |
|
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds |
|
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry |
|
Electromagnetic Waves | Hydrocarbons |
|
Optics | Organic Compounds Containing Halogens |
|
Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation | Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen |
|
Atoms and Nuclei | Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen |
|
Electronic Devices | Biomolecules |
|
Experimental Skills | Principles Related to Practical Chemistry |
|
The chapters carrying high weightage in the NEET Physics syllabus are as follows:
- Thermodynamcs
- Current Electricity
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
The following table brings the chapter-wise weightage of NEET Physics syllabus based on previous year's analysis.
Name of the chapter | Number of questions asked (Approx.) | Weightage in percent |
|---|---|---|
Alternating current | 1 | 4 |
0-1 | 1.5 | |
Current electricity | 2 | 8 |
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | 2 | 6 |
Electric Charges and Fields | 1 | 4.5 |
Electromagnetic induction | 1 | 4 |
Electromagnetic waves | 1 | 5 |
Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | 1 | 4.5 |
0-1 | 2 | |
Kinetic theory | 1 | 3 |
1 | 3 | |
Magnetism and Matter | 1 | 2.5 |
Mechanical Properties of Fluids | 0-1 | 2 |
Mechanical Properties of Solids | 0-1 | 2 |
Motion in a Plane | 0-1 | 1.5 |
Motion in a Straight Line | 0-1 | 1.5 |
Moving Charges and Magnetism | 1 | 2.5 |
Nuclei | 0-1 | 1.5 |
Oscillations | 0-1 | 1.5 |
Physical World, Units and Measurements | 0-1 | 2 |
Ray optics and optical instruments | 1 | 5 |
Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits | 2 | 6 |
System of Particles and Rotational Motion | 1 | 5 |
Thermal Properties of Matter | 0-1 | 2 |
2 | 9 | |
Wave optics | 1 | 5 |
0-1 | 1.5 | |
Work, Energy and Power | 1 | 4 |
Total | 45 | 100 |
Also Read: NEET Physics Syllabus with Chapter-wise Weightage
The NEET Chemistry syllabus is segragated into Organic, Inorganic and Physical Chemistry chapters. The units covered in these three areas are given below.
Physical Chemistry
Unit I: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Unit II: Atomic Structure
Unit III: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Unit IV: Chemical Thermodynamics
Unit V: Solutions
Unit VI: Equilibrium
Unit VII: Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
Unit VIII: Chemical Kinetics
Inorganic Chemistry
Unit IX: Classification in Elements and Periodicity in Properties
Unit X: p-Block Elements
Unit XI: d and f Block Elements
Unit XII: Coordination Compounds
Organic Chemistry
Unit XIII: Purification and Charactisation of Organic Compounds
Unit XIV: Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
Unit XV: Hydrocarbons
Unit XVI: Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
Unit XVII: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
Unit XIX: Biomolecules
Unit XX: Principles Related to Practical Chemistry
Also Read: NEET Chemistry Syllabus With Chapter-wise Weightage
NEET Biology Syllabus 2026
In this section, we bring to you the topics under each unit of the chapter under the Biology syllabus for NEET.
Unit I: Diversity in Living World
-
What is living?; Biodiversity; Need for classification; Taxonomy & Systematics; Concept of species and taxonomical hierarchy; Binomial nomenclature.
-
Five kingdom classifications; salient features and classification of Monera; Protista and Fungi into major groups; Lichens; Viruses and Viroids.
-
Salient features and classification of plants into major groups - Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms (three to five salient and distinguishing features and at least two examples of each category);.
-
Salient features and classification of animals-nonchordate up to phyla level and chordate up to classes level (three to five salient features and at least two examples)
Unit II: Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants
-
Morphology and modifications; Tissues; Anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: Root, stem, leaf, inflorescence- cymose and recemose, flower, fruit and seed (To be dealt along with the relevant practical of the Practical Syllabus). Family (malvaceae, Cruciferae, leguminoceae, compositae, graminae).
-
Animal tissues; Morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems (digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and reproductive) of an insect (frog). (Brief account only)
Unit III: Cell Structure and Function
-
Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life; Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell; Plant cell and animal cell; Cell envelope, cell membrane, cell wall; Cell organelles-structure and function; Endomembrane system-endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, micro bodies; Cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrioles (ultra structure and function); Nucleus-nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleolus.
-
Chemical constituents of living cells: Biomolecules-structure and function of proteins, carbodydrates, lipids, nucleic acids; Enzymes-types, properties, enzyme action, classification and nomenclature of enzymes.
-
B Cell division: Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance.
Unit IV: Plant Physiology
- Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis as a means of Autotrophic nutrition; Site of photosynthesis take place; pigments involved in Photosynthesis (Elementary idea); Photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis; Cyclic and non cyclic and photophosphorylation; Chemiosmotic hypothesis; Photorespiration C3 and C4 pathways; Factors affecting photosynthesis.
-
Respiration: Exchange gases; Cellular respiration-glycolysis, fermentation (anaerobic), TCA cycle and electron transport system (aerobic); Energy relations- Number of ATP molecules generated; Amphibolic pathways; Respiratory quotient.
-
Plant growth and development: Seed germination; Phases of Plant growth and plant growth rate; Conditions of growth; Differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation; Sequence of developmental process in a plant cell; Growth regulators-auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, ABA.
Unit V: Human physiology
-
Breathing and Respiration: Respiratory organs in animals (recall only); Respiratory system in humans; Mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans-Exchange of gases, transport of gases and regulation of respiration Respiratory volumes; Disorders related to respiration-Asthma, Emphysema, Occupational respiratory disorders.
-
Body fluids and circulation: Composition of blood, blood groups, coagulation of blood; Composition of lymph and its function; Human circulatory system-Structure of human heart and blood vessels; Cardiac cycle, cardiac output, ECG, Double circulation; Regulation of cardiac activity; Disorders of circulatory system-Hypertension, Coronary artery disease, Angina pectoris, Heart failure.
-
Excretory products and their elimination: Modes of excretion- Ammonotelism, ureotelism, uricotelism; Human excretory system-structure and fuction; Urine formation, Osmoregulation; Regulation of kidney function-Renin-angiotensin, Atrial Natriuretic Factor, ADH and Diabetes insipidus; Role of other organs in excretion; Disorders; Uraemia, Renal failure, Renal calculi, Nephritis; Dialysis and artificial kidney.
-
Locomotion and Movement: Types of movement- ciliary, fiagellar, muscular; Skeletal musclecontractile proteins and muscle contraction; Skeletal system and its functions (To be dealt with the relevant practical of Practical syllabus); Joints; Disorders of muscular and skeletal systemMyasthenia gravis, Tetany, Muscular dystrophy, Arthritis, Osteoporosis, Gout.
-
Neural control and coordination: Neuron and nerves; Nervous system in humanscentral nervous system, peripheral nervous system and visceral nervous system; Generation and conduction of nerve impulse; Reflex action; Sense organs; Elementary structure and function of eye and ear.
-
Chemical coordination and regulation: Endocrine glands and hormones; Human endocrine systemHypothalamus, Pituitary, Pineal, Thyroid, Parathyroid, Adrenal, Pancreas, Gonads; Mechanism of hormone action (Elementary Idea); Role of hormones as messengers and regulators, Hypo-and hyperactivity and related disorders (Common disorders e.g. Dwarfism, Acromegaly, Cretinism, goiter, exopthalmic goiter, diabetes, Addison’s disease). (Imp: Diseases and disorders mentioned above to be dealt in brief.)
Unit VI: Reproduction
-
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants: Flower structure; Development of male and female gametophytes; Pollination-types, agencies and examples; Outbreeding devices; Pollen-Pistil interaction; Double fertilization; Post fertilization events- Development of endosperm and embryo, Development of seed and formation of fruit; Special modes-apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed and fruit formation.
-
Human Reproduction: Male and female reproductive systems; Microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; Gametogenesis-spermatogenesis & oogenesis; Menstrual cycle; Fertilisation, embryo development upto blastocyst formation, implantation; Pregnancy and placenta formation (Elementary idea); Parturition (Elementary idea); Lactation (Elementary idea).
-
Reproductive health: Need for reproductive health and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STD); Birth control-Need and Methods, Contraception and Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP); Amniocentesis; Infertility and assisted reproductive technologies – IVF, ZIFT, GIFT (Elementary idea for general awareness)
Unit VII: Genetics and Evolution
-
Heredity and variation: Mendelian Inheritance; Deviations from Mendelism- Incomplete dominance, Co-dominance, Multiple alleles and Inheritance of blood groups, Pleiotropy; Elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; Chromosome theory of inheritance; Chromosomes and genes; Sex determination-In humans, birds, honey bee; Linkage and crossing over; Sex linked inheritance-Haemophilia, Colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans-Thalassemia; Chromosomal disorders in humans; Down’s syndrome, Turner’s and Klinefelter’s syndromes.
-
Molecular basis of Inheritance: Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; DNA replication; Central dogma; Transcription, genetic code, translation; Gene expression and regulation- Lac Operon; Genome and human genome project; DNA finger printing, protein biosynthesis.
-
Evolution: Origin of life; Biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution from Paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidence); Darwin’s contribution, Modern Synthetic theory of Evolution; Mechanism of evolution-Variation (Mutation and Recombination) and Natural Selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy-Weinberg’s principle; Adaptive Radiation; Human evolution.
Unit VIII: Biology and Human Welfare
-
Health and Disease; Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (Malaria, Filariasis, Ascariasis. Typhoid, Pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ring worm); Basic concepts of immunologyvaccines; Cancer, HIV and AIDS; Adolescence, drug and alcohol abuse, Tobacco abuse.
-
Improvement in food production; Plant breeding, tissue culture, single cell protein, Biofortification; Apiculture and Animal husbandry.
-
Microbes in human welfare: In household food processing, industrial production, sewage treatment, energy generation and as biocontrol agents and biofertilizers.
Unit IX: Biotechnology and Its Applications
-
Principles and process of Biotechnology: Genetic engineering (Recombinant DNA technology).
-
Application of Biotechnology in Health and Agriculture: Human insulin and vaccine production, gene therapy; Genetically modified organisms-Bt crops; Transgenic Animals; Biosafety issuesBiopiracy and patents.
Unit X: Ecology and Environment
- Organisms and environment: Population interactions-mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism; Population attributes-growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution.
-
Ecosystem: Patterns, components; productivity and decomposition; Energy flow; Pyramids of number, biomass, energy.
-
Biodiversity and its conservation: Concept of Biodiversity; Patterns of Biodiversity; Importance of Biodiversity; Loss of Biodiversity; Biodiversity conservation; Hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, biosphere reserves, National parks and sanctuaries, Sacred Groves.
-
Environmental issues: Air pollution and its control; Water pollution and its control; Agrochemicals and their effects; Solid waste management; Radioactive waste management; Greenhouse effect and global warming; Ozone depletion; Deforestation; Any three case studies as success stories addressing environmental issues.
NEET Biology Syllabus PDF 2026
With the NEET 2026 scheduled on May 3, 2026, it is high time that aspirants should complete the Biology syllabus. Download the NEET Biology syllabus PDF 2026 below.
| Download: NEET Biology Syllabus 2026 |

NEET Syllabus Biology 2026 for Botany & Zoology
The Biology section of NEET exam is segregated into Botany and Zoology. Have a look at the NEET Botany and Zoology topics below-
| NEET Botany Syllabus 2026 |
NEET Zoology Syllaus 2026 |
|---|---|
| Cell - The Unit of Life |
Structural Organization in Animals (including Frog) |
| Cell Cycle and Cell Division |
Biomolecules |
| The Living World |
Breathing and Exchange of Gases |
| Biological Classification |
Body Fluids and Circulation |
| Plant Kingdom |
Excretory Products & their Elimination |
| Morphology of Flowering Plants |
Locomotion & Movement |
| Anatomy of Flowering Plants |
Neural Control & Coordination |
| Photosynthesis in Higher Plants |
Chemical Coordination & Integration |
| Respiration in Plants |
Animal Kingdom |
| Plant Growth and Development |
Human Reproduction |
| Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant |
Reproductive Health |
| Principle of Inheritance and Variation |
Evolution |
| Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
Human Health and Diseases |
| Microbes in Human Welfare |
Biotechnology: Principles & Processes |
| Organisms and Population |
|
| Ecosystem |
|
| Biodiversity and Conservation |
|
Commonly asked questions
The National Medical Commission (NMC) removed some topics from NEET syllabus in 2024. There are around nine chapters in Chemistry which have been removed. In Chemistry, these chapters or topics were removed from the units given in the table below.
Units | Topics |
|---|---|
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | General Introduction: Important and scope of chemistry. |
Atomic number, isotopes and isobars, Concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light. | |
Important compounds of silicon and a few uses: silicon tetrachloride, silicones, silicates and zeolites, their uses. | |
Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen | Cyanides and Isocyanides- will be mentioned at relevant places. |
Environmental Chemistry | Environmental pollution: Air, water and soil pollution, chemical reactions in atmosphere, smogs, major atmospheric pollutants; acid rain ozone and its reactions, effects of depletion of ozone layer, greenhouse effect and global warming-pollution due to industrial wastes; green chemistry as an alternative tool for reducing pollution, strategy for control of environmental pollution. |
Polymers | Classification- Natural and synthetic, methods of polymerization (addition and condensation), copolymerization. Some important polymers: natural and synthetic like polyesters, bakelite; rubber, Biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers. |
Chemistry in Everyday Life | Chemicals in medicines- analgesics, tranquilizers, antiseptics, disinfectants, antimicrobials, antifertility drugs, antibiotics, antacids, antihistamines. |
Surface Chemistry | Adsorption-physisorption and chemisorption; factors affecting adsorption of gases on solids, |
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | · Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C –X bond, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of substitution reactions. Optical rotation. · Haloarenes: Nature of C-X bond, substitution reactions (directive influence of halogen for · Uses and environmental effects of – dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform, freons, DDT.
|
Also Read:
NEET Chemistry Syllabus With Chapter-wise Weightage
The chance of a NEET question coming out of syllabus is low. As per the previous years' analysis, the questions were within the NEET syllabus only and the topics or chapters were evenly distributed. In case candidates encounter any question which is out of the syllabus, they must report it to the invigilator. In case test-takers know the answer and is sure of the accuracy, then they can attempt the question. Otherwise, they should leave the question unattempted. If it is proved that the question is out of NEET 2024 syllabus, NTA would cancel the question and award full marks to the candidates.
The National Testing Agency added some topics to the NEET exam syllabus in 2024. The chapters added to the syllabus are a part of curriculum in several state boards- Maharashtra, Bihar, Jammu and Kashmir, Nagaland and Manipur.
Explore colleges based on NEET
NEET Biology Chapter Wise Weightage 2026
The table brings the topics from the NEET Biology syllabus in NEET along with their weightage.
| Biology Chapters and Topics |
Average No. of Questions from the Chapter |
Weightage of the Chapter and Topic |
|---|---|---|
| Botany |
50 |
100% |
| Cell Biology Cell Division Nucleus Plastids |
4 2 1 1 |
8% 4% 2% 2% |
| Ecology-Biodiversity and Conservation Introduction, Level of biodiversity, Pattern of biodiversity, Loss of biodiversity Conservation of biodiversity |
5 4 1 |
10% 8% 2% |
| Plant Kingdom Plant Kingdom - Algae |
1 |
2% |
| Genetics - I Introduction, Mendelism, Monohybrid cross, Dihybrid cross, Back cross, Test cross, |
4 |
8% |
| Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Pollination Fertilization and embryogenesis, Seed and Polyembryony |
3 2 1 |
6% 4% 2% |
| Ecology-Ecosystem Productivity, Decomposition, Energy flow, Food chain, Food web, Ecological pyramids |
1 |
2% |
| Anatomy of Flowering Plants Plant Tissues, Tissue Systems |
3 |
6% |
| Biotechnology Principles of Biotechnology Applications of Biotechnology in Agriculture Processes of Biotechnology |
4 2 1 1 |
8% 4% 2% 2% |
| Morphology of Flowering Plants Flower |
4 |
8% |
| Plant Physiology - Plant Growth and Growth Hormones Growth and Development Introduction, Discovering of PGR, Auxin, Gibberellins and |
4 2 2 |
8% 4% 4% |
| Plant Physiology-II-Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Dark Reaction C3-cycle, C4 cycle, Photorespiration, CAM-cycle and Factors |
3 |
6% |
| Genetics-II DNA Replication, Transcription, Genetic code and Translation Regulation of gene expression, HGP and DNA fingerprinting |
4 3 1 |
8% 6% 2% |
| Biomolecule-I Lipids Proteins |
2 1 1 |
4% 2% 2% |
| Ecology-Organisms and Population Adaptations, Population and Population interactions, Biotic community |
1 |
2% |
| Plant Physiology-II-Respiration in plants Aerobic respiration- Link reaction and Krebs cycle, Terminal oxidation, Respiratory balance sheet, Amphibolic pathway, Anaerobic respiration-fermentation, Respiratory quotient |
2 2 |
4% 4% |
| Biomolecule-II Enzymes |
2 |
4% |
| Biology In Human Welfare Microbes in Human Welfare |
1 |
2% |
| Biological Classification Kingdom-Fungi |
2 |
4% |
| Zoology |
50 |
100% |
| Cell Biology Cell Division Plastids Mitochondria |
4 2 1 1 |
8% 4% 2% 2% |
| Genetics-I Introduction, Mendelism, Monohybrid cross, Dihybrid cross, Back cross, Test cross, Incomplete dominance, Codominance, Multiple allelism, Pleiotropy Mutation, Pedigree analysis, Genetic disorders |
2 1 1 |
4% 2% 2% |
| Biotechnology Process of Biotechnology Applications of Biotechnology in Medicine, Transgenic Animals |
4 3 1 |
8% 6% 2% |
| Genetics - II DNA Replication, Transcription, Genetic code and |
2 |
4% |
| Ecology-Organisms and Population Adaptations, Population and Population interactions, Biotic community |
1 |
2% |
| Biomolecule - II Enzymes
|
2 |
4% |
| Body fluids and circulation Heart and conduction Blood pressure, ECG |
2 1 1 |
4% 2% 2% |
| Animal Kingdom - I Porifera Arthropoda |
3 1 2 |
6% 2% 4%
|
| Human Reproduction and Reproductive Health Reproductive Health Female Reproductive System Gametogenesis, Reproductive cycles Fertilization, Embryonic, development |
7 2 2 2 1 |
14% 4% 4% 4% 2% |
| Excretory Products and Their Elimination Uriniferous tubule/Nephrons |
2 |
4% |
| Neural Control and Coordination CSF, Brain covering, Brain Cavity Brain and Spinal cord |
2 1 1 |
4% 2% 2% |
| Locomotion and Movement Muscles Joints |
2 1 1 |
4% 2% 2% |
| Biology In Human Welfare-Human Health and Disease Diseases caused by virus Diseases caused by bacteria Immune System and Common Human Disease Drug addiction |
5 1 1 2 1 |
10% 2% 2% 4% 2% |
| Breathing and Exchange of Gases Respiratory volume and capacity Exchange and transport of gases |
2 1 1 |
4% 2% 2% |
| Origin and Evolution Evidences of Evolution Theories of Evolution |
4 1 3 |
8% 2% 6% |
| Chemical Coordination and Integration Mode of action of Hormones Thyroid gland |
2 1 1 |
4% 2% 2% |
| Structural Organisation in Animal Epithelial tissue |
1 |
2% |
| Animal Kingdom - II Chordarta Cyclostomata/Pisces |
3 1 2 |
6% 2% 4% |
Note: The above table carries topic-wise weightages based on last year's NEET exam. Candidates may use it for reference by omitting the removed topics.
List of Deleted Chapters of NEET Biology Syllabus
The chapters were removed from the NEET Biology syllabus in 2024.
| Unit | Chapters |
|---|---|
| Diversity in Living World | Three domains of life, Tools for study of Taxonomy – Museums, Zoos, Herbaria, Botanical gardens |
| Plant Physiology |
|
| Human Physiology | Digestion and absorption; Alimentary canal and digestive glands; Role of digestive enzymes and Neural Control and Coordination: Reflex action; Sense organs; Elementary structure and function of eye and ear. |
| Reproduction | Reproduction in organisms: Reproduction, a characteristic feature of all organisms for the continuation of the species; Modes of reproduction – Asexual and sexual; Asexual reproduction; Modes-Binary fission, sporulation, budding, gemmule, fragmentation; vegetative propagation in plants. |
| Biology and Human Welfare | Improvement in food production; Plant breeding, tissue culture, single cell protein, Biofortification; Apiculture and Animal husbandry. |
| Ecology and Environment | Organisms and environment: Habitat and niche; Population and ecological adaptations Nutrient cycling (carbon and phosphorus); Ecological succession; Ecological Services-Carbon fixation, pollination, oxygen release Environmental issues: Air pollution and its control; Water pollution and its control; Agrochemicals |
Best Books to Prepare for NEET Biology Syllabus
The best books to prepare for the NEET Biology syllabus are given below:
- NCERT Biology Books for Class 11 and Class 12
- Biology by Trueman (Volume 1 and 2)
- Objective Botany by Ansari
- Pradeep Guide on Biology
- G R Bathla publications for Biology
- Moderns ABC of Biology for XI and XII by B B Arora, A K Sabharwal (Modern Publishers)
- Exploring Biology (Vol 1 and 2) by Sanjay Sharma and Sudhakar Banerjee (Arihant Publications)
- Objective Biology (Vol 1, 2 and 3) by K N Bhatia/ K Bhatia (Dinesh Publications)
- Medical Entrances Biology (Vol 1, 2 and 3) Mamta R Solanki and Lalita Ghotik (Target Publications)
- Together with Biology by S Venugopal
NEET Biology Syllabus 2026 Analysis
As per the NEET exam analysis, Biology questions in NEET are mostly NCERT-based. Questions were mostly from topics such as Human Physiology, Genetics, and Plant Physiology. Unlike previous years, this year's question papers featured six figure-based and three direction-based questions, along with 30 'match the following' and 17 statement-based questions. As 30 per cent of the questions were of the 'match the following' type, some students found the paper a bit lengthy. The infographic brings the weightage of NEET Biology questions for Class 11 and Class 12.
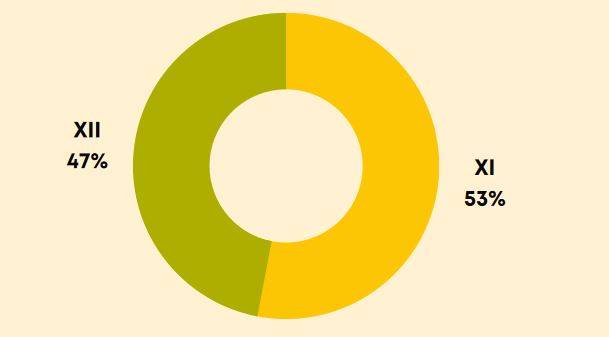
How to Prepare for NEET Biology 2026?
Biology is one of the easiest subjects of NEET and studying for the NEET 2025 Biology syllabus would require sincerity and determination, along with conceptual clarity. Here are a few tips for NEET 2025 Biology preparation.
- Refer to the right books: Students must complete the NCERT Biology textbooks first to develop the foundational knowledge, or to complete fundamental preparation. After that, they may move on to other advanced books,
- Use visual learning techniques: Since Biology is all about diagrams, using visual learning techniques like using flashcards, drawing diagrams and labelling important parts, making notes and highlighting the important points, to name a few.
- Solving NEET previous years questions, mock tests: NEET question papers give the right exposure to students in terms of the question types and topics covered in the NEET Biology syllabus. It also serves as a proper practice material, along with taking regular NEET mock tests.
- Regular revision: Regular revision is the key to any exam preparation. As soon as you complete a topic, you should revise and brush up on the knowledge acquired. Regular revision will ensure that you do not forget the topics that you had prepared a while ago.
- Make a timetable: Since NEET preparation involves studying multiple subjects, it is of utmost importance to strike a balance. Here, preparing a timetable comes in handy, wherein students will allot a proper schedule to study, revise, and practice the NEET Biology syllabus.
The NEET exam pattern has undergone changes. Instead of 200 minutes, the exam will now have 180 minutes. There will not be any optional questions in the NEET exam, unlike the previous years. The NEET question paper will carry 180 questions, all of which are mandatory to attempt. Each subject will have 45 questions. The Biology subject will have 90 questions in total, wherein Botany and Zoology will have 45 questions each.
Read More:

News & Updates
Explore Other Exams
Jun '20 | AIIMS MBBS 2020 Results |
May '20 | AIIMS MBBS 2020 Exam |
Jun '20 | JIPMER 2020 exam (tentative) |
29 Jan '26 | FMGE 2025 December Session Res... |
17 Jan '26 | FMGE 2025 Exam December Sessio... |
22 Mar '26 | OJEE 2026: Last date of fee pa... |
25 Apr '26 | OJEE 2026 Admit Card Release |
Jul '22 | DAVV CET 2022 Registration |
14 Nov '25 - 22 Apr '26 | PU CET (UG) 2026 Application F... |
24 Apr '26 | PU CET (UG) 2026 Registration ... |
Mar '26 | CUET PG 2026 Exam Date |
Apr '26 | NTA JIPMAT 2026 Exam Date |
Student Forum
Answered Yesterday
No, the NEET-UG 2026 registrations have been closed at this point. The last date to register for the aforementioned entrance exam was March 11th 2026. However, candidates can still try to apply for Silver Oak College of Pharmacy BPharm admissions as the institute does not mention NEET-UG as a mandat
S
Contributor-Level 10
Answered Yesterday
Silver Oak College of Pharmacy has not mentioned NEET-UG as a madatory entrance exam for BPharm admissions. Generally, BPharm admissions do not require candidates to appear for the NEET-UG exam to qualify for admissions.
Candidates should connect with the admission desk of Silver Oak College of Pharm
S
Contributor-Level 10
Answered 2 days ago
Candidates must fulfill the Odisha NEET eligibility 2026 to appear for the counselling. To be eligible for NEET Odisha Counselling, candidates must fulfill these criteria-
- Must be at least 17 years old
- Must have passed Class 12 with Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and English (50% aggregate for General,
P
Contributor-Level 6
Answered 2 days ago
The NEET eligibility criteria states that students who have passed Class 12 with Physics, Chemistry, Biology / Biotechnology along with English even as additional subjects from recognised boards and Mathematics/ other elective subject with English at a level not less than the core course for English
V
Contributor-Level 6
Answered 2 days ago
The NEET 2026 exam will be held on May 3, 2026. The NTA will conduct the NEET UG 2026 exam offline in pen and pape mode from 2.00 pm to 5.00 pm.
R
Contributor-Level 6
Answered 3 days ago
Candidates can use the NEET correction window using the process shared below-
Visit neet.nta.nic.in.
Log in with the NEET login details.
Click on 'Correction in Application Form'. link.
- Enter the OTP for verification.
Make the necessary changes.
Save and download the updated Application Confirmation form.
M
Contributor-Level 6
Answered 3 days ago
The NTA has announced the NEET application correction dates 2026. The NEET correction window is available from March 12 to 14, 2026. Candidates can make changes during the these three days.
P
Contributor-Level 6
Answered 3 days ago
Admissions to the BAMS course at BHU is based on the AYUSH counselling process. The lowest NEET score accepted for the BAMS course for admission at BHU was 30748 for the General AI category.
Note: Other categories will have different cutoffs accordingly.
N
Contributor-Level 10
Answered 3 days ago
Shakuntla School of Nursing accepts NEET scores for admission to BSc Nursing course. However, it is not compulsory. Aspirants can also get admission in BSc Nursing based on their GGSIPU CET scores.
N
Guide-Level 15
Answered 3 days ago
BHU NEET cutoff 2025 was published for admission to various AI categories for courses, like MBBS, BDS, and BSc in Nursing. Whether a 470 is a good NEET score would depend entirely on the category you belong to.
For the General AI category, the overall cutoff varied between 1165 and 82615. Hence, stu
N
Contributor-Level 10
 Exam On - 3 May '26
Exam On - 3 May '26




With MA in English, Rupali has more than 15 years of editorial experience. At Shiksha.com, a subsidiary of Info Edge (India) Limited, she creates content and make prep guides for students preparing for competitive e
Read Full Bio