
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2025-26: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) released the CBSE 12th Syllabus 2025-26 on March 29, 2025, on its official website at cbseacademic.nic.in. Students preparing for the CBSE Exam Class 12 2026 can check the updated CBSE Class 12 syllabus 2026 on this page. The CBSE Class 12 exams are conducted covering the entire CBSE Class XII Syllabus 2026. The CBSE Class 12 exam 2026 will be conducted from February 17, 2026. The subject-wise CBSE Class XII syllabus 2026 download links are provided below. Students must download them to check the topics and units that are coming in their final board exams.
Latest: CBSE 12th Syllabus 2025-26 OUT: Know Major Changes
The board has also introduced new skill electives for CBSE Class 12 students to diversify their learning experience. These include:
-
Land Transportation Associate
-
Electronics and Hardware
-
Physical Activity Trainer
-
Design Thinking and Innovation
Important Changes in the Class 12 Syllabus:
-
9-Point Grading Scale: Similar to Class 10, the Class 12 syllabus will also be assessed using the 9-point grading system.
-
Elective Choices: Students can choose one subject from Informatics Practices, Computer Science, or Information Technology (only one of the three)
- How to download the CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2025-26?
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2025-26
- CBSE 12th English Core Syllabus 2025-26
- CBSE 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26
- CBSE 12th Mathematics Syllabus 2025-26
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2025-26 for all subjects: Download PDF
- FAQs on CBSE 12th Syllabus 2026
How to download the CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2025-26?
- Visit the official website cbse.nic.in or click on the subject-wise links provided below
- Click on CBSE 12th Syllabus 2026 subject-wise
- The syllabus will open up on the screen
- Download and save it on the system
- Refer to it to study all the topics
Students must go through the entire CBSE Class 12 syllabus 2026 and strategize their study schedule accordingly. Students must also refer to the CBSE exam class 12 Pattern 2026 to know the marking scheme and the type of questions asked, among other things. The CBSE 12th Class Datesheet 2026 is expected to be released in November 2025 in online mode on the official website-cbse.nic.in. The exams will likely be held between Feb 17 and Apr 4, 2026. After going through the entire CBSE 12th Syllabus 2026 and CBSE Exam Pattern, students must ensure that they solve as many CBSE Exam Class 12 sample papers/previous years' question papers to self-analyze their preparation. Students can also go through the CBSE Class 12 2026 preparation tips for Class 12 to know how to approach the board examinations 2026.
CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2025-26
Students can check below the Chapter and units covered in the CBSE 12th Physics syllabus 2026.
| Unit | Chapter |
|---|---|
| Unit - 1: Electrostatics | Chapter 1: : Electric Charges and Fields Electric charges, Conservation of charge, Coulomb's law-force between two- point charges, forces between multiple charges; superposition principle and continuous charge distribution. Electric field, electric field due to a point charge, electric field lines, electric dipole, electric field due to a dipole, torque on a dipole in uniform electric field. Electric flux, statement of Gauss's theorem and its applications to find field due to infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field inside and outside). Chapter–2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Electric potential, potential difference, electric potential due to a point charge, a dipole and system of charges; equipotential surfaces, electrical potential energy of a system of two-point charges and of electric dipole in an electrostatic field. Conductors and insulators, free charges and bound charges inside a conductor. Dielectrics and electric polarization, capacitors and capacitance, combination of capacitors in series and in parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates, energy stored in a capacitor (no derivation, formulae only). |
| Unit - 2: Current Electricity | Chapter–3: Current Electricity Electric current, flow of electric charges in a metallic conductor, drift velocity, mobility and their relation with electric current; Ohm's law, V-I characteristics (linear and non-linear), electrical energy and power, electrical resistivity and conductivity, temperature dependence of resistance, Internal resistance of a cell, potential difference and emf of a cell, combination of cells in series and in parallel, Kirchhoff's rules, Wheatstone bridge. |
| Unit - 3: Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | Chapter–4: Moving Charges and Magnetism Concept of magnetic field, Oersted's experiment. Biot - Savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop. Ampere's law and its applications to infinitely long straight wire. Straight solenoid (only qualitative treatment), force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields. Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field, force between two parallel current-carrying conductors-definition of ampere, torque experienced by a current loop in uniform magnetic field; Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment, moving coil galvanometer- its current sensitivity and conversion to ammeter and voltmeter. Chapter–5: Magnetism and Matter Bar magnet, bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid (qualitative treatment only), magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and perpendicular to its axis (qualitative treatment only), torque on a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) in a uniform magnetic field (qualitative treatment only), magnetic field lines. Magnetic properties of materials- Para-, dia- and ferro – magnetic substances with examples, Magnetization of materials, effect of temperature on magnetic properties. |
| Unit - 4: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | Chapter–6: Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic induction; Faraday's laws, induced EMF and current; Lenz's Law, Self and mutual induction. Chapter–7: Alternating Current Alternating currents, peak and RMS value of alternating current/voltage; reactance and impedance; LCR series circuit (phasors only), resonance, power in AC circuits, power factor, wattless current. AC generator, Transformer. |
| Unit - 5: Electromagnetic waves | Chapter–8: Electromagnetic Waves Basic idea of displacement current, Electromagnetic waves, their characteristics, their transverse nature (qualitative idea only). Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays) including elementary facts about their uses. |
| Unit - 6: Optics | Chapter–9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Ray Optics: Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula, refraction of light, total internal reflection and optical fibers, refraction at spherical surfaces, lenses, thin lens formula, lens maker’s formula, magnification, power of a lens, combination of thin lenses in contact, refraction of light through a prism. Optical instruments: Microscopes and astronomical telescopes (reflecting and refracting) and their magnifying powers. Chapter–10: Wave Optics Wave optics: Wave front and Huygen’s principle, reflection and refraction of plane wave at a plane surface using wave fronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using Huygen’s principle. Interference, Young's double slit experiment and expression for fringe width (No derivation final expression only), coherent sources and sustained interference of light, diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maxima (qualitative treatment only). |
| Unit - 7: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | Chapter–11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Dual nature of radiation, Photoelectric effect, Hertz and Lenard's observations; Einstein's photoelectric equation-particle nature of light. Experimental study of photoelectric effect Matter waves-wave nature of particles, de-Broglie relation. |
| Unit - 8: Atoms and Nuclei | Chapter–12: Atoms Alpha-particle scattering experiment; Rutherford's model of atom; Bohr model of hydrogen atom, Expression for radius of nth possible orbit, velocity and energy of electron in nth orbit, hydrogen line spectra (qualitative treatment only). Chapter–13: Nuclei Composition and size of nucleus, nuclear force Mass-energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number; nuclear fission, nuclear fusion. |
| Unit - 9: Electronic Devices | Chapter–14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits Energy bands in conductors, semiconductors and insulators (qualitative ideas only) Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors- p and n type, p-n junction NCERT Solutions for Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits |
Also read:
CBSE 12th English Core Syllabus 2025-26
Students can check below the CBSE Class 12 English marking scheme 2026. They can click below to download the complete CBSE 12th English Syllabus 2026-
Section A
Reading Skills-22 Marks
I. Reading Comprehension through Unseen Passage 12+10 = 22 Marks
1. One unseen passage to assess comprehension, interpretation, analysis and inference.
Vocabulary assessment will also be assessed via inference. The passage may be factual, descriptive or literary.
2. One unseen case-based factual passage with verbal/visual inputs like statistical data, charts etc. to assess comprehension, interpretation, analysis, inference and evaluation.
Note: The combined word limit for both passages will be 700-750 words.
Multiple Choice Questions/Objective Type Questions and Short Answer Type Questions (to
be answered in 40-50 words) will be asked.
Section B
Creative Writing Skills-18 Marks
3. Notice, up to 50 words. One out of the two given questions to be answered.
(4 Marks: Format :1 / Content: 2 / Accuracy of Spelling and Grammar: 1).
4. Formal/Informal Invitation and Reply, up to 50 words. One out of the two given questions to be answered. (4 Marks: Format: 1 / Content: 2 / Accuracy of Spelling and Grammar :1).
5. Letters based on verbal/visual input, to be answered in approximately 120-150 words. Letter types include application for a job with bio data or resume. Letters to the editor (giving suggestions or opinion on issues of public interest). One out of the two given questions to be answered. (5 Marks: Format: 1/Organisation of Ideas:1/Content:2/ Accuracy of Spelling and Grammar :1).
6. Article/ Report Writing, descriptive and analytical in nature, based on verbal inputs, to be answered in 120-150 words. One out of the two given questions to be answered.
(5 Marks:Format:1/Organisation of Ideas:1/Content:2/Accuracy of Spelling and Grammar:1).
Section C
Literature Text Book and Supplementary Reading Text- 40 Marks
This section will have variety of assessment items including Multiple Choice Questions, Objective Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions and Long-Answer-Type-Questions to assess comprehension, interpretation, analysis, evaluation and extrapolation beyond the text.
7. One Poetry extract out of two, from the book Flamingo, to assess comprehension, interpretation, analysis, inference and appreciation. (6x1=6 Marks)
8. One Prose extract out of two, from the book Vistas, to assess comprehension, interpretation, analysis, evaluation and appreciation. (4x1=4 Marks)
9. One prose extract out of two from the book Flamingo, to assess comprehension, interpretation, analysis, inference and evaluation. (6x1=6Marks)
10. Short answer type questions (from Prose and Poetry from the book Flamingo), to be answered in 40-50 words each. Questions should elicit inferential responses through critical thinking. Five questions out of the six given, are to be answered. (5x2=10 Marks)
11. Short answer type questions, from Prose (Vistas), to be answered in 40- 50 words each. Questions should elicit inferential responses through critical thinking. Any two out of three questions to be done. (2x2=4 Marks)
12. One Long-answer-type question, from Prose/Poetry (Flamingo), to be answered in 120-150 words. Questions can be based on incident / theme / passage / extract / event as reference points to assess extrapolation beyond and across the text. The question will elicit analytical and evaluative response from the student. Any one out of two questions to be done. (1x5=5 Marks)
13. One long-answer-type-question, based on the chapters from the book Vistas, to be answered in 120-150 words, to assess global comprehension and extrapolation beyond the text. Questions to provide analytical and evaluative responses using incidents, events, themes, as reference points. Any one out of two questions to be done. (1x5=5 Marks)
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT
Assessment of Listening Skills - 05 marks.
Assessment of Speaking Skills - 05 marks.
Project Work - 10 marks.
CBSE 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26
Students can check below the Chapter and units covered in the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry syllabus 2026.
| Units | Chapters/Topics |
|---|---|
| Unit 1: Solutions | Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, solubility of gases in |
| Unit 2: Electrochemistry | Redox reactions, EMF of a cell, standard electrode potential, Nernst equation and its application to |
| Unit 3: Chemical Kinetics | Rate of a reaction (Average and instantaneous), factors affecting rate of reaction: concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction, rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations and half-life (only for zero and first order reactions), concept of collision theory (elementary idea, no mathematical treatment), activation energy, Arrhenius equation. |
Unit 4: d -and f -Block Elements |
General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first row transition metals – metallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, colour, catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy formation, preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4. Lanthanides - Electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity and lanthanides contraction and its consequences. Actinides - Electronic configuration, oxidation states and comparison with lanthanides. |
| Unit 5: Coordination Compounds | Coordination compounds - Introduction, ligands, coordination number, colour, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds. Bonding, Werner's theory, VBT, and CFT; structure and stereoisomerism, importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative analysis, extraction of metals and biological system). |
| Unit 6: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C–X bond, physical and chemical properties, optical rotation mechanism of substitution reactions. Uses and environmental effects of - dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, |
| Unit 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers | Alcohols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (of primary alcohols only), identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols, mechanism of dehydration, uses with special reference to methanol and ethanol. Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophillic substitution reactions, uses of phenols. Ethers: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses. |
| Unit 8: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | Aldehydes and Ketones: Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of nucleophilic addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes, uses. Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses. |
| Unit 9: Amines | Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Diazonium salts: Preparation, chemical reactions and importance in synthetic organic chemistry. |
| Unit 10: Biomolecules | Carbohydrates - Classification (aldoses and ketoses), monosaccahrides (glucose and fructose), D-L configuration oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen); Importance of carbohydrates. Proteins -Elementary idea of - amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides, proteins, structure of proteins - primary, secondary, tertiary structure and quaternary structures (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins; enzymes. Hormones - Elementary idea excluding structure. Vitamins - Classification and functions. Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA. |
Download CBSE Class 12 Chemistry syllabus 2026
Also read:
CBSE 12th Mathematics Syllabus 2025-26
Students must go through the CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Syllabus 2026 carefully and cover it on time. The topics and the marks have been mentioned below:
| Units |
Chapters/Topics |
|---|---|
| Unit-I: Relations and Functions |
Types of relations: reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One-to-one and 2. Inverse Trigonometric Functions Definition, range, domain, principal value branch. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions. |
| Unit-II: Algebra
|
1. Matrices Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of inverse, if it exists; (Here all matrices will have real entries). 2. Determinants |
| Unit-III: Calculus |
1. Continuity and Differentiability Continuity and differentiability, chain rule, derivative of composite functions, derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions like sin−1 𝑥, cos−1 𝑥 and tan−1 𝑥, derivative of implicit functions. Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions. Derivatives of logarithmic and exponential functions. Logarithmic differentiation, the derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second-order derivatives. 2. Applications of Derivatives Applications of derivatives: rate of change of quantities, increasing/decreasing functions, maxima and minima (first derivative test motivated geometrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool). Simple problems (that illustrate basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as real-life situations). 3. Integrals Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, Evaluation of simple integrals of the following types and problems based on them. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (without proof). Definite integrals, Basic properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals. 4. Application of the Integrals Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, circles/ parabolas/ellipses (in standard form only) Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Solution |
| Unit-IV: Vectors and Three-dimensional Geometry |
1. Vectors Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines and direction ratios of a vector. Types of vectors (equal, unit, zero, parallel and collinear vectors), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Definition, Geometrical Interpretation, properties and application of scalar (dot) product of vectors, vector (cross) product of vectors. 2. Three-dimensional Geometry Direction cosines and direction ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian equation and vector equation of a line, skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Angle between two lines. |
| Unit-V: Linear Programming Problem |
1. Linear Programming Introduction, related terminology such as constraints, objective function, optimization, graphical method of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions (bounded or unbounded), feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions (up to three non-trivial constraints). |
| Unit-VI: Probability |
1. Probability |
Also Read:
- NCERT Solutions Maths Class 11 Preparation
- Class 12 Maths Chapters with Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Sets
- NCERT Solutions for Trigonometric Functions
- NCERT Solution for Relations & Functions
- NCERT Solutions for Sequence and Series
- NCERT Solutions for Probability
- NCERT Solutions for Limits and Derivatives
- NCERT Solutions for Statistics
- NCERT Solutions for Introduction to Three-dimensional Geometry
Read More:
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2025-26 for all subjects: Download PDF
The cbse. gov. in syllabus 2026 Class 12 was released online in March 2025. The CBSE 10th Syllabus 2026 is released for all subjects. Students can download the updated subject-wise CBSE Syllabus 2026 Class 12 PDF for all streams below:
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2025-26 for Subjects Common to all Streams
| Subject | Syllabus PDF |
|---|---|
| Mathematics | Download PDF |
| Applied Mathematics | Download PDF |
| English Core | Download PDF |
| English Elective | Download PDF |
| Hindi Core | Download PDF |
| Hindi Elective | Download PDF |
CBSE 12th Syllabus 2026 for Science subjects
| Subjects | Syllabus PDF |
|---|---|
| Physics | Download PDF |
| Biology | Download PDF |
| Chemistry | Download PDF |
| Biotechnology | Download PDF |
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2026 for Commerce subjects
| Subjects | Syllabus PDF |
|---|---|
| Accountancy | Download PDF |
| Business Studies | Download PDF |
| Economics | Download PDF |
| Computer Science | Download PDF |
CBSE 12th Syllabus 2026 for Arts subjects
| Subjects | Syllabus PDF |
|---|---|
| Sociology | Download PDF |
| History | Download PDF |
| Psychology | Download PDF |
| Political science | Download PDF |
| Home Science | Download PDF |
| Geography | Download PDF |
CBSE has provided the CBSE class 12th syllabus for all subjects on its official website. Students can download it by clicking on the links provided below and start learning and practicing it to score better.
Also Read: NCERT Solutions Class 11
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2026 for other subjects
| Subject | Syllabus PDF |
|---|---|
| Arabic | Download PDF |
| Assamese | Download PDF |
| Bengali | Download PDF |
| Bhoti | Download PDF |
| Bhutia | Download PDF |
| Bodo | Download PDF |
| French | Download PDF |
| German | Download PDF |
| Gujarati | Download PDF |
| Japanese | Download PDF |
| Kannada | Download PDF |
| Kashmiri | Download PDF |
| Kokborok | Download PDF |
| Lepcha | Download PDF |
| Limboo | Download PDF |
| Malayalam | Download PDF |
| Manipuri | Download PDF |
| Marathi | Download PDF |
| Mizo | Download PDF |
| Nepali | Download PDF |
| Odia | Download PDF |
| Persian | Download PDF |
| Punjabi | Download PDF |
| Russian | Download PDF |
| Sanskrit Core | Download PDF |
| Sanskrit Elective | Download PDF |
| Telugu AP | Telugu Telangana | Download PDF | Download PDF |
| Tibetan | Download PDF |
| Urdu Core | Download PDF |
| Urdu elective | Download PDF |
| Carnatic Melodic | Download PDF |
| Carnatic Vocal | Download PDF |
| Carnatic Percussion | Download PDF |
| Entrepreneurship | Download PDF |
| Engineering Graphics | Download PDF |
| Fine Arts | Download PDF |
| Indian Classical Dance | Download PDF |
| Hindustani Melodic | Download PDF |
| Hindustani Vocal | Download PDF |
| Hindustani Percussion | Download PDF |
| Informatics Practices | Download PDF |
| Knowledge Traditions & Practices of India | Download PDF |
| Legal studies | Download PDF |
| NCC | Download PDF |
| Physical Education | Download PDF |
| Health & Physical Education | Download PDF |
| Work experience | Download PDF |
| General Studies | Download PDF |
| Tangkhul | Download PDF |
| Tamil | Download PDF |
| Spanish | Download PDF |
| Sindhi | Download PDF |
FAQs on CBSE 12th Syllabus 2026
Students can check the FAQs related to CBSE 12th syllabus 2026 below:
Explore subject-wise topics asked in CBSE 12th
Select your preferred subject
Explore top Science exams
1 Feb '26 - 25 Feb '26 | JEE Main 2026 Registration Ses... |
10 Jan '26 - 12 Feb '26 | MHT CET 2026 Application Form ... |
6 Apr '26 - 2 May '26 | JEE Advanced 2026 registration... |
10 Nov '25 - 8 Apr '26 | KIITEE 2026 Registration - Pha... |
2 Feb '26 - 31 Mar '26 | IPU CET 2026 Application Form... |
15 Dec '25 - 16 Mar '26 | BITSAT 2026 Application Form S... |
24 Oct '25 - 31 Mar '26 | VITEEE 2026 application form |
3 Feb '26 - 16 Mar '26 | COMEDK Application Form 2026 |
5 Mar '26 - 13 Apr '26 | IISER Aptitude Test 2026 Regis... |
CBSE 12th Exam
Student Forum
Answered Yesterday
The IISER application form 2026 will be available online. Completed 12th grade from a recognised board can apply. Steps to apply for IISER after 12th are registration, form filling, payment of exam fees, and download of the confirmation letter.
V
Contributor-Level 9
Answered 2 days ago
Any stream can choose this course, There is no specific stream required to be eligible for this course
A
Beginner-Level 1
Answered 3 days ago
For admissions to universities abroad to undergraduate courses, a PTE score between 51-60 is generally considered sufficient. However, higher scores can lead you to win an atractive scholarship or get selected in a good college.
R
Contributor-Level 8
Answered 4 days ago
Yes, Indian students can definitely study on scholarship in South Korea after 12th. There are various scholarships available for students from India including-
- Global Korea Scholarship or GKS Scholarship
- University-Specific Scholarships
- Private Scholarships
To increase your chances of securing a scholar
A
Contributor-Level 8
Answered 6 days ago
International students who have completed their 12 from a board that the university considers with an advanced test like IIT JEE or STEP are allowed in the university. Students should also appear for ACT/ SAT test and submit English language requirements to get UG admission.
N
Contributor-Level 9
Answered a week ago
Bro, the best course is to take BSC in artificial intelligencxe and BSC in data Science because it has very huge job oppurtunity in market, AAFT Noida provides degree in these domain and provides placement. here are good teachers who are experienced in good company
A
Beginner-Level 5
Answered a week ago
To gain admission to Lovely Professional University (LPU) after 12th, students need to first choose their desired undergraduate program, such as B.Tech, BBA, BCA, B.Sc, B.Com, or B.Arch. Admissions are generally based on either qualifying exam marks (10+2 results) or entrance tests. Most programs re
V
Contributor-Level 10
Answered 2 weeks ago
The best 1-year Diploma course after 12th is mentioned below.
- Diploma in Operation Theatre (OT) Management.
- Diploma in Medical Nursing Assistant.
- Diploma in Computer Science.
- Diploma in Fashion Designing.
- Diploma in Cybersecurity.
- Diploma in Hardware networking.
- Diploma in Interior Design.
- Diploma in Comput
V
Contributor-Level 9
Answered 2 weeks ago
If you wish to go into the field of forensic Science after your 12th, make sure you focus on PCM/PCB subjects and score well as many colleges take admissions based on that merit or appear for the accepted entrance exam. You can aim for a reputed college to pursue a BSc in Forensic Science followed b
D
Contributor-Level 10
Answered 2 weeks ago
It's difficult but in some colleges you may can get
S
Beginner-Level 1
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test

 Exam On - 17 Feb '26 - 5 Mar '26
Exam On - 17 Feb '26 - 5 Mar '26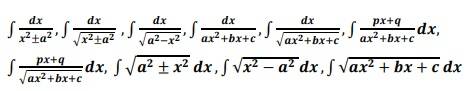

How to apply for IISER after 12th?